Influence of Demographic Factors on Clinical Outcomes in Adults With Chronic Idiopathic Constipation Treated With Plecanatide
- PMID: 37162147
- PMCID: PMC10371318
- DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000598
Influence of Demographic Factors on Clinical Outcomes in Adults With Chronic Idiopathic Constipation Treated With Plecanatide
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC) is a common condition that affects some patient groups more often. Demographic/clinical characteristics can differ in presentation and therapeutic response. The impact of these characteristics on plecanatide efficacy/safety was examined.
Methods: Data from 2 identically designed, randomized, phase 3 trials of adults with CIC receiving 3 mg of plecanatide, 6 mg of plecanatide, or placebo for 12 weeks were analyzed. Subgroups were baseline age, body mass index (BMI), race/ethnicity, and sex/gender. Endpoints included durable overall complete spontaneous bowel movement (CSBM) responder rate, weekly CSBMs and spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs), and adverse events.
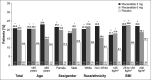
Results: Overall (N = 2,639; 3 mg of plecanatide [n = 877]; 6 mg of plecanatide [n = 877]; and placebo [n = 885]), CSBM responder rates were significantly greater with 3 mg of plecanatide and 6 mg of plecanatide vs placebo in subgroups with those younger than 65 years ( P < 0.001), females ( P < 0.001), White individuals ( P < 0.001), and BMI <25 kg/m 2 ( P ≤ 0.004) and 25-30 kg/m 2 ( P < 0.001); as well, for 3 mg: 65 years or older ( P = 0.03), non-White individuals ( P < 0.001), and BMI ≥30 kg/m 2 ( P = 0.02). Improvement from baseline in weekly CSBM and SBM frequency occurred in all subgroups for both plecanatide doses vs placebo ( P ≤ 0.02) at week 12, except those aged 65 years or older for 6 mg of plecanatide. The most common adverse event was diarrhea (3 mg [4.9%]; 6 mg [5.4%]; and placebo [1.3%]).
Discussion: Pooled data from identically designed CIC trials strengthened the ability to identify meaningful subgroup comparisons regarding plecanatide efficacy and safety.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01982240.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American College of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Suares NC, Ford AC. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic idiopathic constipation in the community: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106(9):1582–91; quiz 1, 92. - PubMed
-
- Palsson OS, Whitehead W, Törnblom H, et al. Prevalence of Rome IV functional bowel disorders among adults in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. Gastroenterology 2020;158(5):1262–73.e3. - PubMed
-
- Sperber AD, Bangdiwala SI, Drossman DA, et al. Worldwide prevalence and burden of functional gastrointestinal disorders, results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology 2021;160(1):99–114.e3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

