Wearable Graphene-based smart face mask for Real-Time human respiration monitoring
- PMID: 37162811
- PMCID: PMC10151252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111970
Wearable Graphene-based smart face mask for Real-Time human respiration monitoring
Abstract
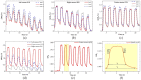
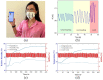
After the pandemic of SARS-CoV-2, the use of face-masks is considered the most effective way to prevent the spread of virus-containing respiratory fluid. As the virus targets the lungs directly, causing shortness of breath, continuous respiratory monitoring is crucial for evaluating health status. Therefore, the need for a smart face mask (SFM) capable of wirelessly monitoring human respiration in real-time has gained enormous attention. However, some challenges in developing these devices should be solved to make practical use of them possible. One key issue is to design a wearable SFM that is biocompatible and has fast responsivity for non-invasive and real-time tracking of respiration signals. Herein, we present a cost-effective and straightforward solution to produce innovative SFMs by depositing graphene-based coatings over commercial surgical masks. In particular, graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) are integrated into a polycaprolactone (PCL) polymeric matrix. The resulting SFMs are characterized morphologically, and their electrical, electromechanical, and sensing properties are fully assessed. The proposed SFM exhibits remarkable durability (greater than1000 cycles) and excellent fast response time (∼42 ms), providing simultaneously normal and abnormal breath signals with clear differentiation. Finally, a developed mobile application monitors the mask wearer's breathing pattern wirelessly and provides alerts without compromising user-friendliness and comfort.
Keywords: Graphene and Advanced materials; Piezoresistive sensor; Real-time monitoring; Respiration monitoring; Smart face mask; Wearable sensing device.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures





References
-
- Alshabouna F. PEDOT:PSS-modified cotton conductive thread for mass manufacturing of textilebased electrical wearable sensors by computerized embroidery. Mater. Today. 2022
-
- J.J. Freundlich, J.C. Erickson, Electrical Impedance Pneumography for Simple Nonrestrictive Continuous Monitoring of Respiratory Rate, Rhythm and Tidal Volume for Surgical Patients*, n.d. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
