Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 37163623
- PMCID: PMC10257898
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2212851
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The efficacy and safety of treatment with cabozantinib in combination with nivolumab and ipilimumab in patients with previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma are unknown.
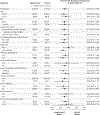
Methods: In this phase 3, double-blind trial, we enrolled patients with advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma who had not previously received treatment and had intermediate or poor prognostic risk according to the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium categories. Patients were randomly assigned to receive 40 mg of cabozantinib daily in addition to nivolumab and ipilimumab (experimental group) or matched placebo in addition to nivolumab and ipilimumab (control group). Nivolumab (3 mg per kilogram of body weight) and ipilimumab (1 mg per kilogram) were administered once every 3 weeks for four cycles. Patients then received nivolumab maintenance therapy (480 mg once every 4 weeks) for up to 2 years. The primary end point was progression-free survival, as determined by blinded independent review according to Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, version 1.1, and was assessed in the first 550 patients who had undergone randomization. The secondary end point was overall survival, assessed in all patients who had undergone randomization.
Results: Overall, 855 patients underwent randomization: 428 were assigned to the experimental group and 427 to the control group. Among the first 550 patients who had undergone randomization (276 in the experimental group and 274 in the control group), the probability of progression-free survival at 12 months was 0.57 in the experimental group and 0.49 in the control group (hazard ratio for disease progression or death, 0.73; 95% confidence interval, 0.57 to 0.94; P = 0.01); 43% of the patients in the experimental group and 36% in the control group had a response. Grade 3 or 4 adverse events occurred in 79% of the patients in the experimental group and in 56% in the control group. Follow-up for overall survival is ongoing.
Conclusions: Among patients with previously untreated, advanced renal-cell carcinoma who had intermediate or poor prognostic risk, treatment with cabozantinib plus nivolumab and ipilimumab resulted in significantly longer progression-free survival than treatment with nivolumab and ipilimumab alone. Grade 3 or 4 adverse events were more common in the experimental group than in the control group. (Funded by Exelixis; COSMIC-313 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03937219.).
Copyright © 2023 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Re: Toni K. Choueiri, Thomas Powles, Laurence Albiges, et al. Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2023;388:1767-78.Eur Urol. 2023 Oct;84(4):e93. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2023.06.027. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Eur Urol. 2023. PMID: 37442718 No abstract available.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 3;389(5):476. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306786. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37530832 No abstract available.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 3;389(5):476. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306786. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37530833 No abstract available.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 3;389(5):476-477. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306786. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37530834 No abstract available.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 3;389(5):477. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306786. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37530835 No abstract available.
-
Cabozantinib plus Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 3;389(5):477-478. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2306786. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 37530836 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
