Solvent-Dependent Structural Dynamics in the Ultrafast Photodissociation Reaction of Triiodide Observed with Time-Resolved X-ray Solution Scattering
- PMID: 37163700
- PMCID: PMC10375522
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c00484
Solvent-Dependent Structural Dynamics in the Ultrafast Photodissociation Reaction of Triiodide Observed with Time-Resolved X-ray Solution Scattering
Abstract
Resolving the structural dynamics of bond breaking, bond formation, and solvation is required for a deeper understanding of solution-phase chemical reactions. In this work, we investigate the photodissociation of triiodide in four solvents using femtosecond time-resolved X-ray solution scattering following 400 nm photoexcitation. Structural analysis of the scattering data resolves the solvent-dependent structural evolution during the bond cleavage, internal rearrangements, solvent-cage escape, and bond reformation in real time. The nature and structure of the reaction intermediates during the recombination are determined, elucidating the full mechanism of photodissociation and recombination on ultrafast time scales. We resolve the structure of the precursor state for recombination as a geminate pair. Further, we determine the size of the solvent cages from the refined structures of the radical pair. The observed structural dynamics present a comprehensive picture of the solvent influence on structure and dynamics of dissociation reactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
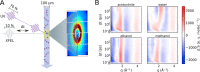

 ,
,  , and
α were optimized.
, and
α were optimized.

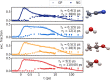
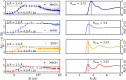
 , illustrating
the bond dissociation. From
the initial increase, the speed of dissociation, vd, is estimated (for ethanol, the data point at t = 0.4 ps was excluded from the speed estimate). Right:
Radial distribution functions of the solvent O atoms (C for acetonitrile)
around the I atoms in their ground state I3– structure. Solvents from top to bottom: acetonitrile, water, ethanol,
and methanol.
, illustrating
the bond dissociation. From
the initial increase, the speed of dissociation, vd, is estimated (for ethanol, the data point at t = 0.4 ps was excluded from the speed estimate). Right:
Radial distribution functions of the solvent O atoms (C for acetonitrile)
around the I atoms in their ground state I3– structure. Solvents from top to bottom: acetonitrile, water, ethanol,
and methanol.
References
-
- Bagchi B.; Oxtoby D. W.; Fleming G. R. Theory of the time development of the stokes shift in polar media. Chem. Phys. 1984, 86, 257–267. 10.1016/0301-0104(84)80014-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

