In situ architecture of the ER-mitochondria encounter structure
- PMID: 37165187
- PMCID: PMC7614606
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06050-3
In situ architecture of the ER-mitochondria encounter structure
Abstract
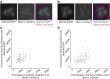
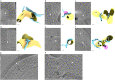
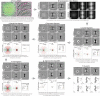
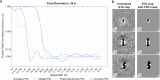
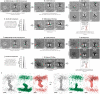
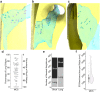
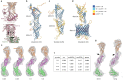
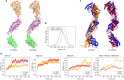
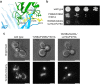
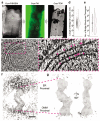
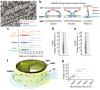
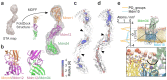
The endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria are main hubs of eukaryotic membrane biogenesis that rely on lipid exchange via membrane contact sites1-3, but the underpinning mechanisms remain poorly understood. In yeast, tethering and lipid transfer between the two organelles is mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria encounter structure (ERMES), a four-subunit complex of unresolved stoichiometry and architecture4-6. Here we determined the molecular organization of ERMES within Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells using integrative structural biology by combining quantitative live imaging, cryo-correlative microscopy, subtomogram averaging and molecular modelling. We found that ERMES assembles into approximately 25 discrete bridge-like complexes distributed irregularly across a contact site. Each bridge consists of three synaptotagmin-like mitochondrial lipid binding protein domains oriented in a zig-zag arrangement. Our molecular model of ERMES reveals a pathway for lipids. These findings resolve the in situ supramolecular architecture of a major inter-organelle lipid transfer machinery and provide a basis for the mechanistic understanding of lipid fluxes in eukaryotic cells.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Vance JE. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7248–7256. - PubMed
-
- Vance JE. Newly made phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine are preferentially translocated between rat liver mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Achleitner G, et al. Association between the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria of yeast facilitates interorganelle transport of phospholipids through membrane contact. Eur J Biochem. 1999;264:545–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

