The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle
- PMID: 37165455
- PMCID: PMC10173583
- DOI: 10.1186/s40104-023-00876-7
The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle
Abstract
Background: A detailed understanding of genetic variants that affect beef merit helps maximize the efficiency of breeding for improved production merit in beef cattle. To prioritize the putative variants and genes, we ran a comprehensive genome-wide association studies (GWAS) analysis for 21 agronomic traits using imputed whole-genome variants in Simmental beef cattle. Then, we applied expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) mapping between the genotype variants and transcriptome of three tissues (longissimus dorsi muscle, backfat, and liver) in 120 cattle.
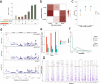
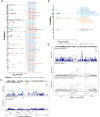
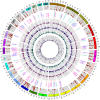
Results: We identified 1,580 association signals for 21 beef agronomic traits using GWAS. We then illuminated 854,498 cis-eQTLs for 6,017 genes and 46,970 trans-eQTLs for 1,903 genes in three tissues and built a synergistic network by integrating transcriptomics with agronomic traits. These cis-eQTLs were preferentially close to the transcription start site and enriched in functional regulatory regions. We observed an average of 43.5% improvement in cis-eQTL discovery using multi-tissue eQTL mapping. Fine-mapping analysis revealed that 111, 192, and 194 variants were most likely to be causative to regulate gene expression in backfat, liver, and muscle, respectively. The transcriptome-wide association studies identified 722 genes significantly associated with 11 agronomic traits. Via the colocalization and Mendelian randomization analyses, we found that eQTLs of several genes were associated with the GWAS signals of agronomic traits in three tissues, which included genes, such as NADSYN1, NDUFS3, LTF and KIFC2 in liver, GRAMD1C, TMTC2 and ZNF613 in backfat, as well as TIGAR, NDUFS3 and L3HYPDH in muscle that could serve as the candidate genes for economic traits.
Conclusions: The extensive atlas of GWAS, eQTL, fine-mapping, and transcriptome-wide association studies aid in the suggestion of potentially functional variants and genes in cattle agronomic traits and will be an invaluable source for genomics and breeding in beef cattle.
Keywords: Cattle; Colocalization; GWAS; TWAS; eQTL mapping.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Grisart B, Farnir F, Karim L, Cambisano N, Kim J-J, Kvasz A, et al. Genetic and functional confirmation of the causality of the DGAT1 K232A quantitative trait nucleotide in affecting milk yield and composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(8):2398–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0308518100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2020-YWF-YB-02/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund
- 32202652/the Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CARS-37/China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- 2020GG0210/Science and Technology Project of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

