Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction model performance decreases with long-term antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 37165622
- PMCID: PMC10366790
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2023.0121
Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction model performance decreases with long-term antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients
Abstract
Background/aims: Existing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) prediction models are derived mainly from pretreatment or early on-treatment parameters. We reassessed the dynamic changes in the performance of 17 HCC models in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) during long-term antiviral therapy (AVT).
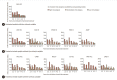
Methods: Among 987 CHB patients administered long-term entecavir therapy, 660 patients had 8 years of follow-up data. Model scores were calculated using on-treatment values at 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, and 5 years of AVT to predict threeyear HCC occurrence. Model performance was assessed with the area under the receiver operating curve (AUROC). The original model cutoffs to distinguish different levels of HCC risk were evaluated by the log-rank test.
Results: The AUROCs of the 17 HCC models varied from 0.51 to 0.78 when using on-treatment scores from years 2.5 to 5. Models with a cirrhosis variable showed numerically higher AUROCs (pooled at 0.65-0.73 for treated, untreated, or mixed treatment models) than models without (treated or mixed models: 0.61-0.68; untreated models: 0.51-0.59). Stratification into low, intermediate, and high-risk levels using the original cutoff values could no longer reflect the true HCC incidence using scores after 3.5 years of AVT for models without cirrhosis and after 4 years of AVT for models with cirrhosis.
Conclusion: The performance of existing HCC prediction models, especially models without the cirrhosis variable, decreased in CHB patients on long-term AVT. The optimization of existing models or the development of novel models for better HCC prediction during long-term AVT is warranted.
Keywords: Antiviral treatment; Carcinoma, hepatocellular; External validation; Hepatitis B, chronic; Prediction model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflictsto disclose.
Figures



Comment in
-
Decreasing performance of HCC prediction models during antiviral therapy for hepatitis B: what else to keep in mind: Editorial on "Hepatocellular carcinoma prediction model performance decreases with long-term antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B patients".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):656-658. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0499. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38973181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Yip TC, Wong GL, Chan HL, Tse YK, Lam KL, Lui GC, et al. HBsAg seroclearance further reduces hepatocellular carcinoma risk after complete viral suppression with nucleos(t)ide analogues. J Hepatol. 2019;70:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Su TH, Hu TH, Chen CY, Huang YH, Chuang WL, Lin CC, et al. Four-year entecavir therapy reduces hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhotic events and mortality in chronic hepatitis B patients. Liver Int. 2016;36:1755–1764. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Zhou J, Wu X, Sun Y, Wang B, Kong Y, et al. Comparative performance of 14 HCC prediction models in CHB: A dynamic validation at serial on-treatment timepoints. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:1444–1453. - PubMed
-
- Chan HL, Fung S, Seto WK, Chuang WL, Chen CY, Kim HJ, et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016;1:185-195. Erratum in: Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;1:e2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

