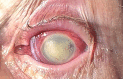
Investigating and Treating a Corneal Ulcer Due to Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 37166191
- PMCID: PMC10358754
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00277-23
Investigating and Treating a Corneal Ulcer Due to Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
Resistant Gram-negative bacteria are a growing concern in the United States, leading to significant morbidity and mortality. We identified a 72-year-old female patient who presented with unilateral vision loss. She was found to have a large corneal ulcer with hypopyon. Culture of corneal scrapings grew extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Treatment involved a combination of systemic and topical antibiotics. Whole genome sequencing revealed the presence of blaVIM-80, blaGES-9, and other resistance determinants. This distinctive organism was linked to an over-the-counter artificial tears product.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibacterial agents; cefiderocol; corneal ulcer; imipenem; keratitis; lubricant eye drops; polymyxin B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extensively and pan-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis: clinical features, risk factors, and outcome.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016 Feb;254(2):315-22. doi: 10.1007/s00417-015-3208-7. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26537122
-
Multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis and its effective treatment with topical colistimethate.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016 Feb;64(2):153-7. doi: 10.4103/0301-4738.179721. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27050354 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Corneal Ulcer Associated With Artificial Tears Eye Drops.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023 May 1;141(5):496. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.1105. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36947092
-
Characterization of virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus spp. strains isolated from corneal infection.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018 Nov;41(9):823-829. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2018.01.012. Epub 2018 Oct 3. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018. PMID: 30292385
-
Overview of mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an ocular perspective.Clin Exp Optom. 2018 Mar;101(2):162-171. doi: 10.1111/cxo.12621. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Clin Exp Optom. 2018. PMID: 29044738 Review.
Cited by
-
Development, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Evaluation of Hybrid Nanoparticles (HNPs) Based on Phospholipids, Cholesterol, Colistin, and Chitosan Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 1;17(2):182. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17020182. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40006549 Free PMC article.
-
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa T3SS can contribute to traversal of an in situ epithelial multilayer independently of the T3SS needle.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0026625. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00266-25. Epub 2025 Mar 14. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40084853 Free PMC article.
-
A biofilm-tropic Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophage uses the exopolysaccharide Psl as receptor.Elife. 2025 Aug 11;13:RP102352. doi: 10.7554/eLife.102352. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40788302 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Topical Cefiderocol Treatment of Experimental Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis Is Dependent upon the State of the Corneal Epithelium.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Oct 17;13(10):979. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13100979. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452245 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 selectively drives IL-1β secretion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa infected neutrophils and regulates corneal disease severity.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 20;14(1):5832. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41391-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37730693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2019. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2023. Outbreak of extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with artificial tears. https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2023/han00485.asp. Accessed 3 February 2023.
-
- Kohler P, Tijet N, Kim HC, Johnstone J, Edge T, Patel SN, Seah C, Willey B, Coleman B, Green K, Armstrong I, Katz K, Muller MP, Powis J, Poutanen SM, Richardson D, Sarabia A, Simor A, McGeer A, Melano RG, Toronto Invasive Bacterial Diseases Network (TIBDN) . 2020. Dissemination of Verona integron-encoded metallo-beta-lactamase among clinical and environmental Enterobacteriaceae isolates in Ontario, Canada. Sci Rep 10:18580. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-75247-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous