High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma organoids as models of chromosomal instability
- PMID: 37166279
- PMCID: PMC10174694
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.83867
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma organoids as models of chromosomal instability
Abstract
High-grade serous ovarian carcinoma (HGSOC) is the most genomically complex cancer, characterized by ubiquitous TP53 mutation, profound chromosomal instability, and heterogeneity. The mutational processes driving chromosomal instability in HGSOC can be distinguished by specific copy number signatures. To develop clinically relevant models of these mutational processes we derived 15 continuous HGSOC patient-derived organoids (PDOs) and characterized them using bulk transcriptomic, bulk genomic, single-cell genomic, and drug sensitivity assays. We show that HGSOC PDOs comprise communities of different clonal populations and represent models of different causes of chromosomal instability including homologous recombination deficiency, chromothripsis, tandem-duplicator phenotype, and whole genome duplication. We also show that these PDOs can be used as exploratory tools to study transcriptional effects of copy number alterations as well as compound-sensitivity tests. In summary, HGSOC PDO cultures provide validated genomic models for studies of specific mutational processes and precision therapeutics.
Keywords: cancer biology; chromosomal instability; genetics; genomics; high-grade serous ovarian cancer; human; organoids.
© 2023, Vias, Morrill Gavarró et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MV, LM, CS, DS, DC, SB, BH, MS, JH, FC No competing interests declared, AP, FM, GM, JB GM, FM, AMP and JDB are founders and shareholders of Tailor Bio Ltd
Figures

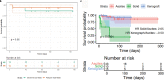












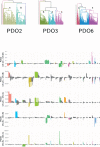




Update of
References
-
- Aaltonen LA, Abascal F, Abeshouse A, Aburatani H, Adams DJ, Agrawal N, Ahn KS, Ahn S-M, Aikata H, Akbani R, Akdemir KC, Al-Ahmadie H, Al-Sedairy ST, Al-Shahrour F, Alawi M, Albert M, Aldape K, Alexandrov LB, Ally A, Alsop K, Alvarez EG, Amary F, Amin SB, Aminou B, Ammerpohl O, Anderson MJ, Ang Y, Antonello D, Anur P, Aparicio S, Appelbaum EL, Arai Y, Aretz A, Arihiro K, Ariizumi S, Armenia J, Arnould L, Asa S, Assenov Y, Atwal G, Aukema S, Auman JT, Aure MRR, Awadalla P, Aymerich M, Bader GD, Baez-Ortega A, Bailey MH, Bailey PJ, Balasundaram M, Balu S, Bandopadhayay P, Banks RE, Barbi S, Barbour AP, Barenboim J, Barnholtz-Sloan J, Barr H, Barrera E, Bartlett J, Bartolome J, Bassi C, Bathe OF, Baumhoer D, Bavi P, Baylin SB, Bazant W, Beardsmore D, Beck TA, Behjati S, Behren A, Niu B, Bell C, Beltran S, Benz C, Berchuck A, Bergmann AK, Bergstrom EN, Berman BP, Berney DM, Bernhart SH, Beroukhim R, Berrios M, Bersani S, Bertl J, Betancourt M, Bhandari V, Bhosle SG, Biankin AV, Bieg M, Bigner D, Binder H, Birney E, Birrer M, Biswas NK, Bjerkehagen B, Bodenheimer T, Boice L, Bonizzato G, De Bono JS, Boot A, Bootwalla MS, Borg A, Borkhardt A, Boroevich KA, Borozan I, Borst C, Bosenberg M, Bosio M, Boultwood J, Bourque G, Boutros PC, Bova GS, Bowen DT, Bowlby R, Bowtell DDL, Boyault S, Boyce R, Boyd J, Brazma A, Brennan P, Brewer DS, Brinkman AB, Bristow RG, Broaddus RR, Brock JE, Brock M, Broeks A, Brooks AN, Brooks D, Brors B, Brunak S, Bruxner TJC, Bruzos AL, Buchanan A, Buchhalter I, Buchholz C, Bullman S, Burke H, Burkhardt B, Burns KH, Busanovich J, Bustamante CD, Butler AP, Butte AJ, Byrne NJ, Børresen-Dale A-L, Caesar-Johnson SJ, Cafferkey A, Cahill D, Calabrese C, Caldas C, Calvo F, Camacho N, Campbell PJ, Campo E, Cantù C, Cao S, Carey TE, Carlevaro-Fita J, Carlsen R, Cataldo I, Cazzola M, Cebon J, Cerfolio R, Chadwick DE, Chakravarty D, Chalmers D, Chan CWY, Chan K, Chan-Seng-Yue M, Chandan VS, Chang DK, Chanock SJ, Chantrill LA, Chateigner A, Chatterjee N, Chayama K, Chen H-W, Chen J, Chen K, Chen Y, Chen Z, Cherniack AD, Chien J, Chiew Y-E, Chin S-F, Cho J, Cho S, Choi JK, Choi W, Chomienne C, Chong Z, Choo SP, Chou A, Christ AN, Christie EL, Chuah E, Cibulskis C, Cibulskis K, Cingarlini S, Clapham P, Claviez A, Cleary S, Cloonan N, Cmero M, Collins CC, Connor AA, Cooke SL, Cooper CS, Cope L, Corbo V, Cordes MG, Cordner SM, Cortés-Ciriano I, Covington K, Cowin PA, Craft B, Craft D, Creighton CJ, Cun Y, Curley E, Cutcutache I, Czajka K, Czerniak B, Dagg RA, Danilova L, Davi MV, Davidson NR, Davies H, Davis IJ, Davis-Dusenbery BN, Dawson KJ, De La Vega FM, De Paoli-Iseppi R, Defreitas T, Tos APD, Delaneau O, Demchok JA, Demeulemeester J, Demidov GM, Demircioğlu D, Dennis NM, Denroche RE, Dentro SC, Desai N, Deshpande V, Deshwar AG, Desmedt C, Deu-Pons J, Dhalla N, Dhani NC, Dhingra P, Dhir R, DiBiase A, Diamanti K, Ding L, Ding S, Dinh HQ, Dirix L, Doddapaneni H, Donmez N, Dow MT, Drapkin R, Drechsel O, Drews RM, Serge S, Dudderidge T, Dueso-Barroso A, Dunford AJ, Dunn M, Dursi LJ, Duthie FR, Dutton-Regester K, Eagles J, Easton DF, Edmonds S, Edwards PA, Edwards SE, Eeles RA, Ehinger A, Eils J, Eils R, El-Naggar A, Eldridge M, Ellrott K, Erkek S, Escaramis G, Espiritu SMG, Estivill X, Etemadmoghadam D, Eyfjord JE, Faltas BM, Fan D, Fan Y, Faquin WC, Farcas C, Fassan M, Fatima A, Favero F, Fayzullaev N, Felau I, Fereday S, Ferguson ML, Ferretti V, Feuerbach L, Field MA, Fink JL, Finocchiaro G, Fisher C, Fittall MW, Fitzgerald A, Fitzgerald RC, Flanagan AM, Fleshner NE, Flicek P, Foekens JA, Fong KM, Fonseca NA, Foster CS, Fox NS, Fraser M, Frazer S, Frenkel-Morgenstern M, Friedman W, Frigola J, Fronick CC, Fujimoto A, Fujita M, Fukayama M, Fulton LA, Fulton RS, Furuta M, Futreal PA, Füllgrabe A, Gabriel SB, Gallinger S, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Gao J, Gao S, Garraway L, Garred Ø, Garrison E, Garsed DW, Gehlenborg N, Gelpi JLL, George J, Gerhard DS, Gerhauser C, Gershenwald JE, Gerstein M, Gerstung M, Getz G, Ghori M, Ghossein R, Giama NH, Gibbs RA, Gibson B, Gill AJ, Gill P, Giri DD, Glodzik D, Gnanapragasam VJ, Goebler ME, Goldman MJ, Gomez C, Gonzalez S, Gonzalez-Perez A, Gordenin DA, Gossage J, Gotoh K, Govindan R, Grabau D, Graham JS, Grant RC, Green AR, Green E, Greger L, Grehan N, Grimaldi S, Grimmond SM, Grossman RL, Grundhoff A, Gundem G, Guo Q, Gupta M, Gupta S, Gut IG, Gut M, Göke J, Ha G, Haake A, Haan D, Haas S, Haase K, Haber JE, Habermann N, Hach F, Haider S, Hama N, Hamdy FC, Hamilton A, Hamilton MP, Han L, Hanna GB, Hansmann M, Haradhvala NJ, Harismendy O, Harliwong I, Harmanci AO, Harrington E, Hasegawa T, Haussler D, Hawkins S, Hayami S, Hayashi S, Hayes DN, Hayes SJ, Hayward NK, Hazell S, He Y, Heath AP, Heath SC, Hedley D, Hegde AM, Heiman DI, Heinold MC, Heins Z, Heisler LE, Hellstrom-Lindberg E, Helmy M, Heo SG, Hepperla AJ, Heredia-Genestar JM, Herrmann C, Hersey P, Hess JM, Hilmarsdottir H, Hinton J, Hirano S, Hiraoka N, Hoadley KA, Hobolth A, Hodzic E, Hoell JI, Hoffmann S, Hofmann O, Holbrook A, Holik AZ, Hollingsworth MA, Holmes O, Holt RA, Hong C, Hong EP, Hong JH, Hooijer GK, Hornshøj H, Hosoda F, Hou Y, Hovestadt V, Howat W, Hoyle AP, Hruban RH, Hu J, Hu T, Hua X, Huang K, Huang M, Huang MN, Huang V, Huang Y, Huber W, Hudson TJ, Hummel M, Hung JA, Huntsman D, Hupp TR, Huse J, Huska MR, Hutter B, Hutter CM, Hübschmann D, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Imbusch CD, Imielinski M, Imoto S, Isaacs WB, Isaev K, Ishikawa S, Iskar M, Islam SMA, Ittmann M, Ivkovic S, Izarzugaza JMG, Jacquemier J, Jakrot V, Jamieson NB, Jang GH, Jang SJ, Jayaseelan JC, Jayasinghe R, Jefferys SR, Jegalian K, Jennings JL, Jeon S-H, Jerman L, Ji Y, Jiao W, Johansson PA, Johns AL, Johns J, Johnson R, Johnson TA, Jolly C, Joly Y, Jonasson JG, Jones CD, Jones DR, Jones DTW, Jones N, Jones SJM, Jonkers J, Ju YS, Juhl H, Jung J, Juul M, Juul RI, Juul S, Jäger N, Kabbe R, Kahles A, Kahraman A, Kaiser VB, Kakavand H, Kalimuthu S, von Kalle C, Kang KJ, Karaszi K, Karlan B, Karlić R, Karsch D, Kasaian K, Kassahn KS, Katai H, Kato M, Katoh H, Kawakami Y, Kay JD, Kazakoff SH, Kazanov MD, Keays M, Kebebew E, Kefford RF, Kellis M, Kench JG, Kennedy CJ, Kerssemakers JNA, Khoo D, Khoo V, Khuntikeo N, Khurana E, Kilpinen H, Kim HK, Kim H-L, Kim H-Y, Kim H, Kim J, Kim J, Kim JK, Kim Y, King TA, Klapper W, Kleinheinz K, Klimczak LJ, Knappskog S, Kneba M, Knoppers BM, Koh Y, Komorowski J, Komura D, Komura M, Kong G, Kool M, Korbel JO, Korchina V, Korshunov A, Koscher M, Koster R, Kote-Jarai Z, Koures A, Kovacevic M, Kremeyer B, Kretzmer H, Kreuz M, Krishnamurthy S, Kube D, Kumar K, Kumar P, Kumar S, Kumar Y, Kundra R, Kübler K, Küppers R, Lagergren J, Lai PH, Laird PW, Lakhani SR, Lalansingh CM, Lalonde E, Lamaze FC, Lambert A, Lander E, Landgraf P, Landoni L, Langerød A, Lanzós A, Larsimont D, Larsson E, Lathrop M, Lau LMS, Lawerenz C, Lawlor RT, Lawrence MS, Lazar AJ, Lazic AM, Le X, Lee D, Lee D, Lee EA, Lee HJ, Lee JJ-K, Lee J-Y, Lee J, Lee MTM, Lee-Six H, Lehmann K-V, Lehrach H, Lenze D, Leonard CR, Leongamornlert DA, Leshchiner I, Letourneau L, Letunic I, Levine DA, Lewis L, Ley T, Li C, Li CH, Li HI, Li J, Li L, Li S, Li S, Li X, Li X, Li X, Li Y, Liang H, Liang S-B, Lichter P, Lin P, Lin Z, Linehan WM, Lingjærde OC, Liu D, Liu EM, Liu F-FF, Liu F, Liu J, Liu X, Livingstone J, Livitz D, Livni N, Lochovsky L, Loeffler M, Long GV, Lopez-Guillermo A, Lou S, Louis DN, Lovat LB, Lu Y, Lu Y-J, Lu Y, Luchini C, Lungu I, Luo X, Luxton HJ, Lynch AG, Lype L, López C, López-Otín C, Ma EZ, Ma Y, MacGrogan G, MacRae S, Macintyre G, Madsen T, Maejima K, Mafficini A, Maglinte DT, Maitra A, Majumder PP, Malcovati L, Malikic S, Malleo G, Mann GJ, Mantovani-Löffler L, Marchal K, Marchegiani G, Mardis ER, Margolin AA, Marin MG, Markowetz F, Markowski J, Marks J, Marques-Bonet T, Marra MA, Marsden L, Martens JWM, Martin S, Martin-Subero JI, Martincorena I, Martinez-Fundichely A, Maruvka YE, Mashl RJ, Massie CE, Matthew TJ, Matthews L, Mayer E, Mayes S, Mayo M, Mbabaali F, McCune K, McDermott U, McGillivray PD, McLellan MD, McPherson JD, McPherson JR, McPherson TA, Meier SR, Meng A, Meng S, Menzies A, Merrett ND, Merson S, Meyerson M, Meyerson W, Mieczkowski PA, Mihaiescu GL, Mijalkovic S, Mikkelsen T, Milella M, Mileshkin L, Miller CA, Miller DK, Miller JK, Mills GB, Milovanovic A, Minner S, Miotto M, Arnau GM, Mirabello L, Mitchell C, Mitchell TJ, Miyano S, Miyoshi N, Mizuno S, Molnár-Gábor F, Moore MJ, Moore RA, Morganella S, Morris QD, Morrison C, Mose LE, Moser CD, Muiños F, Mularoni L, Mungall AJ, Mungall K, Musgrove EA, Mustonen V, Mutch D, Muyas F, Muzny DM, Muñoz A, Myers J, Myklebost O, Möller P, Nagae G, Nagrial AM, Nahal-Bose HK, Nakagama H, Nakagawa H, Nakamura H, Nakamura T, Nakano K, Nandi T, Nangalia J, Nastic M, Navarro A, Navarro FCP, Neal DE, Nettekoven G, Newell F, Newhouse SJ, Newton Y, Ng AWT, Ng A, Nicholson J, Nicol D, Nie Y, Nielsen GP, Nielsen MM, Nik-Zainal S, Noble MS, Nones K, Northcott PA, Notta F, O’Connor BD, O’Donnell P, O’Donovan M, O’Meara S, O’Neill BP, O’Neill JR, Ocana D, Ochoa A, Oesper L, Ogden C, Ohdan H, Ohi K, Ohno-Machado L, Oien KA, Ojesina AI, Ojima H, Okusaka T, Omberg L, Ong CK, Ossowski S, Ott G, Ouellette BFF, P’ng C, Paczkowska M, Paiella S, Pairojkul C, Pajic M, Pan-Hammarström Q, Papaemmanuil E, Papatheodorou I, Paramasivam N, Park JW, Park J-W, Park K, Park K, Park PJ, Parker JS, Parsons SL, Pass H, Pasternack D, Pastore A, Patch AM, Pauporté I, Pea A, Pearson JV, Pedamallu CS, Pedersen JS, Pederzoli P, Peifer M, Pennell NA, Perou CM, Perry MD, Petersen GM, Peto M, Petrelli N, Petryszak R, Pfister SM, Phillips M, Pich O, Pickett HA, Pihl TD, Pillay N, Pinder S, Pinese M, Pinho AV, Pitkänen E, Pivot X, Piñeiro-Yáñez E, Planko L, Plass C, Polak P, Pons T, Popescu I, Potapova O, Prasad A, Preston SR, Prinz M, Pritchard AL, Prokopec SD, Provenzano E, Puente XS, Puig S, Puiggròs M, Pulido-Tamayo S, Pupo GM, Purdie CA, Quinn MC, Rabionet R, Rader JS, Radlwimmer B, Radovic P, Raeder B, Raine KM, Ramakrishna M, Ramakrishnan K, Ramalingam S, Raphael BJ, Rathmell WK, Rausch T, Reifenberger G, Reimand J, Reis-Filho J, Reuter V, Reyes-Salazar I, Reyna MA, Reynolds SM, Rheinbay E, Riazalhosseini Y, Richardson AL, Richter J, Ringel M, Ringnér M, Rino Y, Rippe K, Roach J, Roberts LR, Roberts ND, Roberts SA, Robertson AG, Robertson AJ, Rodriguez JB, Rodriguez-Martin B, Rodríguez-González FG, Roehrl MHA, Rohde M, Rokutan H, Romieu G, Rooman I, Roques T, Rosebrock D, Rosenberg M, Rosenstiel PC, Rosenwald A, Rowe EW, Royo R, Rozen SG, Rubanova Y, Rubin MA, Rubio-Perez C, Rudneva VA, Rusev BC, Ruzzenente A, Rätsch G, Sabarinathan R, Sabelnykova VY, Sadeghi S, Sahinalp SC, Saini N, Saito-Adachi M, Saksena G, Salcedo A, Salgado R, Salichos L, Sallari R, Saller C, Salvia R, Sam M, Samra JS, Sanchez-Vega F, Sander C, Sanders G, Sarin R, Sarrafi I, Sasaki-Oku A, Sauer T, Sauter G, Saw RPM, Scardoni M, Scarlett CJ, Scarpa A, Scelo G, Schadendorf D, Schein JE, Schilhabel MB, Schlesner M, Schlomm T, Schmidt HK, Schramm S-J, Schreiber S, Schultz N, Schumacher SE, Schwarz RF, Scolyer RA, Scott D, Scully R, Seethala R, Segre AV, Selander I, Semple CA, Senbabaoglu Y, Sengupta S, Sereni E, Serra S, Sgroi DC, Shackleton M, Shah NC, Shahabi S, Shang CA, Shang P, Shapira O, Shelton T, Shen C, Shen H, Shepherd R, Shi R, Shi Y, Shiah Y-J, Shibata T, Shih J, Shimizu E, Shimizu K, Shin SJ, Shiraishi Y, Shmaya T, Shmulevich I, Shorser SI, Short C, Shrestha R, Shringarpure SS, Shriver C, Shuai S, Sidiropoulos N, Siebert R, Sieuwerts AM, Sieverling L, Signoretti S, Sikora KO, Simbolo M, Simon R, Simons JV, Simpson JT, Simpson PT, Singer S, Sinnott-Armstrong N, Sipahimalani P, Skelly TJ, Smid M, Smith J, Smith-McCune K, Socci ND, Sofia HJ, Soloway MG, Song L, Sood AK, Sothi S, Sotiriou C, Soulette CM, Span PN, Spellman PT, Sperandio N, Spillane AJ, Spiro O, Spring J, Staaf J, Stadler PF, Staib P, Stark SG, Stebbings L, Stefánsson ÓA, Stegle O, Stein LD, Stenhouse A, Stewart C, Stilgenbauer S, Stobbe MD, Stratton MR, Stretch JR, Struck AJ, Stuart JM, Stunnenberg HG, Su H, Su X, Sun RX, Sungalee S, Susak H, Suzuki A, Sweep F, Szczepanowski M, Sültmann H, Yugawa T, Tam A, Tamborero D, Tan BKT, Tan D, Tan P, Tanaka H, Taniguchi H, Tanskanen TJ, Tarabichi M, Tarnuzzer R, Tarpey P, Taschuk ML, Tatsuno K, Tavaré S, Taylor DF, Taylor-Weiner A, Teague JW, Teh BT, Tembe V, Temes J, Thai K, Thayer SP, Thiessen N, Thomas G, Thomas S, Thompson A, Thompson AM, Thompson JFF, Thompson RH, Thorne H, Thorne LB, Thorogood A, Tiao G, Tijanic N, Timms LE, Tirabosco R, Tojo M, Tommasi S, Toon CW, Toprak UH, Torrents D, Tortora G, Tost J, Totoki Y, Townend D, Traficante N, Treilleux I, Trotta J-R, Trümper LHP, Tsao M, Tsunoda T, Tubio JMC, Tucker O, Turkington R, Turner DJ, Tutt A, Ueno M, Ueno NT, Umbricht C, Umer HM, Underwood TJ, Urban L, Urushidate T, Ushiku T, Uusküla-Reimand L, Valencia A, Van Den Berg DJ, Van Laere S, Van Loo P, Van Meir EG, Van den Eynden GG, Van der Kwast T, Vasudev N, Vazquez M, Vedururu R, Veluvolu U, Vembu S, Verbeke LPC, Vermeulen P, Verrill C, Viari A, Vicente D, Vicentini C, VijayRaghavan K, Viksna J, Vilain RE, Villasante I, Vincent-Salomon A, Visakorpi T, Voet D, Vyas P, Vázquez-García I, Waddell NM, Waddell N, Wadelius C, Wadi L, Wagener R, Wala JA, Wang J, Wang J, Wang L, Wang Q, Wang W, Wang Y, Wang Z, Waring PM, Warnatz H-J, Warrell J, Warren AY, Waszak SM, Wedge DC, Weichenhan D, Weinberger P, Weinstein JN, Weischenfeldt J, Weisenberger DJ, Welch I, Wendl MC, Werner J, Whalley JP, Wheeler DA, Whitaker HC, Wigle D, Wilkerson MD, Williams A, Wilmott JS, Wilson GW, Wilson JM, Wilson RK, Winterhoff B, Wintersinger JA, Wiznerowicz M, Wolf S, Wong BH, Wong T, Wong W, Woo Y, Wood S, Wouters BG, Wright AJ, Wright DW, Wright MH, Wu C-L, Wu D-Y, Wu G, Wu J, Wu K, Wu Y, Wu Z, Xi L, Xia T, Xiang Q, Xiao X, Xing R, Xiong H, Xu Q, Xu Y, Xue H, Yachida S, Yakneen S, Yamaguchi R, Yamaguchi TN, Yamamoto M, Yamamoto S, Yamaue H, Yang F, Yang H, Yang JY, Yang L, Yang L, Yang S, Yang T-P, Yang Y, Yao X, Yaspo M-L, Yates L, Yau C, Ye C, Ye K, Yellapantula VD, Yoon CJ, Yoon S-S, Yousif F, Yu J, Yu K, Yu W, Yu Y, Yuan K, Yuan Y, Yuen D, Yung CK, Zaikova O, Zamora J, Zapatka M, Zenklusen JC, Zenz T, Zeps N, Zhang C-Z, Zhang F, Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhao Z, Zheng L, Zheng X, Zhou W, Zhou Y, Zhu B, Zhu H, Zhu J, Zhu S, Zou L, Zou X, deFazio A, van As N, van Deurzen CHM, van de Vijver MJ, van’t Veer L, von Mering C, The ICGC/TCGA Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes Consortium Pan-Cancer analysis of whole genomes. Nature. 2020;578:82–93. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1969-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed AA, Etemadmoghadam D, Temple J, Lynch AG, Riad M, Sharma R, Stewart C, Fereday S, Caldas C, Defazio A, Bowtell D, Brenton JD. Driver mutations in TP53 are ubiquitous in high grade serous carcinoma of the ovary. The Journal of Pathology. 2010;221:49–56. doi: 10.1002/path.2696. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Aparicio SAJR, Behjati S, Biankin AV, Bignell GR, Bolli N, Borg A, Børresen-Dale A-L, Boyault S, Burkhardt B, Butler AP, Caldas C, Davies HR, Desmedt C, Eils R, Eyfjörd JE, Foekens JA, Greaves M, Hosoda F, Hutter B, Ilicic T, Imbeaud S, Imielinski M, Jäger N, Jones DTW, Jones D, Knappskog S, Kool M, Lakhani SR, López-Otín C, Martin S, Munshi NC, Nakamura H, Northcott PA, Pajic M, Papaemmanuil E, Paradiso A, Pearson JV, Puente XS, Raine K, Ramakrishna M, Richardson AL, Richter J, Rosenstiel P, Schlesner M, Schumacher TN, Span PN, Teague JW, Totoki Y, Tutt ANJ, Valdés-Mas R, van Buuren MM, van ’t Veer L, Vincent-Salomon A, Waddell N, Yates LR, Zucman-Rossi J, Futreal PA, McDermott U, Lichter P, Meyerson M, Grimmond SM, Siebert R, Campo E, Shibata T, Pfister SM, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR, Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome Initiative. ICGC Breast Cancer Consortium. ICGC MMML-Seq Consortium. ICGC PedBrain Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature. 2013;500:415–421. doi: 10.1038/nature12477. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakhoum SF, Ngo B, Laughney AM, Cavallo J-A, Murphy CJ, Ly P, Shah P, Sriram RK, Watkins TBK, Taunk NK, Duran M, Pauli C, Shaw C, Chadalavada K, Rajasekhar VK, Genovese G, Venkatesan S, Birkbak NJ, McGranahan N, Lundquist M, LaPlant Q, Healey JH, Elemento O, Chung CH, Lee NY, Imielenski M, Nanjangud G, Pe’er D, Cleveland DW, Powell SN, Lammerding J, Swanton C, Cantley LC. Chromosomal instability drives metastasis through a cytosolic DNA response. Nature. 2018;553:467–472. doi: 10.1038/nature25432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

