Cyanomethyl Vinyl Ethers Against Naegleria fowleri
- PMID: 37167960
- PMCID: PMC10251482
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00110
Cyanomethyl Vinyl Ethers Against Naegleria fowleri
Abstract
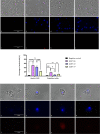
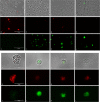
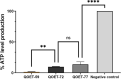
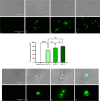
Naegleria fowleri is a pathogenic amoeba that causes a fulminant and rapidly progressive disease affecting the central nervous system called primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). Moreover, the disease is fatal in more than 97% of the reported cases, mostly affecting children and young people after practicing aquatic activities in nontreated fresh and warm water bodies contaminated with these amoebae. Currently, the treatment of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis is based on a combination of different antibiotics and antifungals, which are not entirely effective and lead to numerous side effects. In the recent years, research against PAM is focused on the search of novel, less toxic, and fully effective antiamoebic agents. Previous studies have reported the activity of cyano-substituted molecules in different protozoa. Therefore, the activity of 46 novel synthetic cyanomethyl vinyl ethers (QOET-51 to QOET-96) against two type strains of N. fowleri (ATCC 30808 and ATCC 30215) was determined. The data showed that QOET-51, QOET-59, QOET-64, QOET-67, QOET-72, QOET-77, and QOET-79 were the most active molecules. In fact, the selectivity index (CC50/IC50) was sixfold higher when compared to the activities of the drugs of reference. In addition, the mechanism of action of these compounds was studied, with the aim to demonstrate the induction of a programmed cell death process in N. fowleri.
Keywords: Naegleria fowleri; apoptosis; cyanomethyl vinyl ethers; cytotoxicity; primary amoebic meningoencephalitis; programmed cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
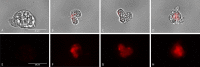
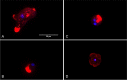
References
-
- Gogate A.; Deodhar L.. Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic Naegleria Fowleri (Aerobia) from a Swimming Pool in Bombay; Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene: England, 1985, p 134. - PubMed
-
- Javanmard E.; Niyyati M.; Lorenzo-Morales J.; Lasjerdi Z.; Behniafar H.; Mirjalali H. Molecular Identification of Waterborne Free Living Amoebae (Acanthamoeba, Naegleria and Vermamoeba) Isolated from Municipal Drinking Water and Environmental Sources, Semnan Province, North Half of Iran. Exp Parasitol 2017, 183, 240–244. 10.1016/j.exppara.2017.09.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

