Prognostic role of pretreatment skeletal muscle index in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 37168049
- PMCID: PMC10164928
- DOI: 10.3389/pore.2023.1611055
Prognostic role of pretreatment skeletal muscle index in gastric cancer patients: A meta-analysis
Abstract
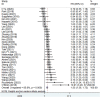
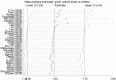
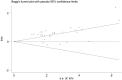
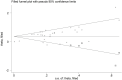
Background: The association between pretreatment skeletal muscle index (SMI) and long-term survival of gastric cancer patients remains unclear up to now. The aim of this meta-analysis was to identify the prognostic value of pretreatment SMI in gastric cancer. Methods: The PubMed, EMBASE and Web of Science electronic databases were searched up to 5 June 2022 for relevant studies. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS) and the second outcomes were disease-free survival (DFS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were combined to assess the relationship between pretreatment SMI and survival of gastric cancer patients. All statistical analyses were conducted by STATA 15.0 software. Results: A total of 31 retrospective studies involving 12,434 patients were enrolled in this meta-analysis. The pooled results demonstrated that lower pretreatment was significantly associated with poorer OS (HR = 1.53, p < 0.001). Besides, lower pretreatment SMI was also related with worse DFS (HR = 1.39, p < 0.001) and CSS (HR = 1.96, p < 0.001). Conclusion: Pretreatment SMI was significantly associated with prognosis of gastric cancer patients and lower SMI predicted worse survival. However, more prospective high-quality studies are still needed to verify our findings.
Keywords: gastric cancer; meta-analysis; pretreatment; prognosis; skeletal muscle index.
Copyright © 2023 He, Zhou, Li, Gou and Jia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Skeletal Muscle Mass Index in Esophageal Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis.Nutr Cancer. 2022;74(10):3592-3600. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2022.2088814. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Nutr Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35730425
-
Prognostic value of pretreatment skeletal muscle index in pancreatic carcinoma patients: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 May 12;102(19):e33663. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033663. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37171343 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of pretreatment skeletal muscle mass index for long-term survival of bladder cancer patients: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 30;18(6):e0288077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288077. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37390088 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in surgical esophageal cancer patients: An updated meta-analysis.Front Surg. 2022 Aug 26;9:922595. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.922595. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36090319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic role of the pretreatment C-reactive protein/albumin ratio in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(10):e19362. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019362. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32150079 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Subcutaneous adipose tissue [18F]FDG uptake and CT-derived body composition variables for predicting survival outcomes in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Apr 24. doi: 10.1007/s00259-025-07296-x. Online ahead of print. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40272500
References
-
- Supportive PDQ. Palliative care editorial B: Nutrition in cancer care (PDQ®): Health professional version. In: PDQ cancer information summaries. edn. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute US; (2002).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

