Calpain-mediated Mechanoptosis in Breast Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37168957
- PMCID: PMC10165377
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10215
Calpain-mediated Mechanoptosis in Breast Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
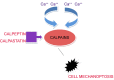
Calpains belong to a family of important calcium-dependent cysteine proteases. They are involved in intracellular processes including cytoskeleton disorganization and substrate proteolysis. They also enhance apoptosis and cell to cell adhesion. Calpains demonstrate also a mechanosensory function in neoplastic and malignant cells due to their implication in mechanoptosis. This is a specific type of apoptotic death induced by strong external mechanical stimuli. Anti-cytoskeleton rigidity inhibition strategies based on calpain induction lead to increased apoptosis of tumor transformed cells. Elevated intracellular calcium concentration mediated by specific receptors and channels activates calpains. In the current molecular review, we explored the role of calpains in calcium-dependent signa transduction pathways in breast adenocarcinoma in conjunction with novel agents that activate their important anti-tumor functions.
Keywords: Calpain; apoptosis; breast adenocarcinoma; mechanoptosis; review.
Copyright 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare in relation to this study.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
