Signal peptide mimicry primes Sec61 for client-selective inhibition
- PMID: 37169961
- PMCID: PMC10449633
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-023-01326-1
Signal peptide mimicry primes Sec61 for client-selective inhibition
Abstract
Preventing the biogenesis of disease-relevant proteins is an attractive therapeutic strategy, but attempts to target essential protein biogenesis factors have been hampered by excessive toxicity. Here we describe KZR-8445, a cyclic depsipeptide that targets the Sec61 translocon and selectively disrupts secretory and membrane protein biogenesis in a signal peptide-dependent manner. KZR-8445 potently inhibits the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in primary immune cells and is highly efficacious in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. A cryogenic electron microscopy structure reveals that KZR-8445 occupies the fully opened Se61 lateral gate and blocks access to the lumenal plug domain. KZR-8445 binding stabilizes the lateral gate helices in a manner that traps select signal peptides in the Sec61 channel and prevents their movement into the lipid bilayer. Our results establish a framework for the structure-guided discovery of novel therapeutics that selectively modulate Sec61-mediated protein biogenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
E.L., J.A., T.M. and C.J.K. are employees and shareholders of Kezar Life Sciences. D.M. is a shareholder of Kezar Life Sciences. J.T. is a founder of Global Blood Therapeutics, Kezar Life Sciences, Cedilla Therapeutics and Terremoto Biosciences, and is a scientific advisor to Entos. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
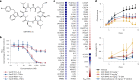
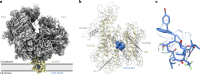
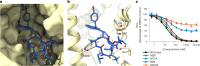

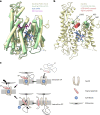



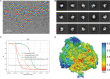
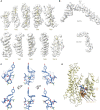

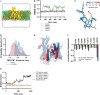
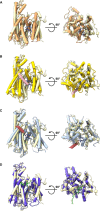
Comment in
-
Inhibiting Sec61-mediated protein translocation.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 Jul;22(7):535. doi: 10.1038/d41573-023-00086-w. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023. PMID: 37253967 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zimmermann R, Eyrisch S, Ahmad M, Helms V. Protein translocation across the ER membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011;1808:912–924. - PubMed
-
- Rapoport TA, Li L, Park E. Structural and mechanistic insights into protein translocation. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017;33:369–390. - PubMed
-
- Manson, L. A. (ed.) Biomembranes Vol 2, pp. 193–195 (Springer, 1971).
-
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J. Mol. Biol. 1985;184:99–105. - PubMed

