Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the angiopoietin-like gene family and their role in lipid metabolism in pigs
- PMID: 37170504
- PMCID: PMC10475376
- DOI: 10.5713/ab.23.0057
Phylogenetic and expression analysis of the angiopoietin-like gene family and their role in lipid metabolism in pigs
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the phylogenetic and expression analysis of the angiopoietin-like (ANGPTL) gene family and their role in lipid metabolism in pigs.
Methods: In this study, the amino acid sequence analysis, phylogenetic analysis, and chromosome adjacent gene analysis were performed to identify the ANGPTL gene family in pigs. According to the body weight data from 60 Jinhua pigs, different tissues of 6 pigs with average body weight were used to determine the expression profile of ANGPTL1-8. The ileum, subcutaneous fat, and liver of 8 pigs with distinct fatness were selected to analyze the gene expression of ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4, and ANGPTL8.
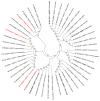
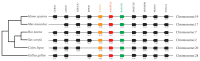
Results: The sequence length of ANGPTLs in pigs was between 1,186 and 1,991 bp, and the pig ANGPTL family members shared common features with human homologous genes, including the high similarity of the amino acid sequence and chromosome flanking genes. Amino acid sequence analysis showed that ANGPTL1-7 had a highly conserved domain except for ANGPTL8. Phylogenetic analysis showed that each ANGPTL homologous gene shared a common origin. Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis showed that ANGPTL family members had different expression patterns in different tissues. ANGPTL3 and ANGPTL8 were mainly expressed in the liver, while ANGPTL4 was expressed in many other tissues, such as the intestine and subcutaneous fat. The expression levels of ANGPTL3 in the liver and ANGPTL4 in the liver, intestine and subcutaneous fat of Jinhua pigs with low propensity for adipogenesis were significantly higher than those of high propensity for adipogenesis.
Conclusion: These results increase our knowledge about the biological role of the ANGPTL family in this important economic species, it will also help to better understand the role of ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4, and ANGPTL8 in lipid metabolism of pigs, and provide innovative ideas for developing strategies to improve meat quality of pigs.
Keywords: Angiopoietin-like Protein; Evolution; Expression; Fat Metabolize; Jinhua Pig.
Conflict of interest statement
We certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Atypical angiopoietin-like protein that regulates ANGPTL3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 27;109(48):19751-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217552109. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23150577 Free PMC article.
-
Association between ANGPTL3, 4, and 8 and lipid and glucose metabolism markers in patients with diabetes.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 22;16(7):e0255147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255147. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34293055 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression level of ANGPTL8 in white adipose tissue under acute and chronic cold treatment.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Sep 26;20(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01547-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34565390 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Function of Angiopoietin-like Protein 3 (ANGPTL3) in Atherosclerosis.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(31):5159-5174. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190621120523. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31223079 Review.
-
Angiopoietin-like proteins 3, 4 and 8: regulating lipid metabolism and providing new hope for metabolic syndrome.J Drug Target. 2014 Sep;22(8):679-87. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2014.928715. Epub 2014 Jun 24. J Drug Target. 2014. PMID: 24960069 Review.
Cited by
-
Circumventing Cardiovascular Calamities: The Dawn of ANGPTL3 Blockade in Severe Dyslipidemia Management.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(2):59-64. doi: 10.2174/011871529X305291240715112812. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 39039670 Review.
References
-
- Aron-Wisnewsky J, Warmbrunn MV, Nieuwdorp M, Clément K. Metabolism and metabolic disorders and the microbiome: the intestinal microbiota associated with obesity, lipid metabolism, and metabolic health-pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:573–99. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.057. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

