Early-life adversity increases morphine tolerance and persistent inflammatory hypersensitivity through upregulation of δ opioid receptors in mice
- PMID: 37171192
- PMCID: PMC10502877
- DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002925
Early-life adversity increases morphine tolerance and persistent inflammatory hypersensitivity through upregulation of δ opioid receptors in mice
Abstract
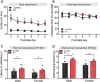
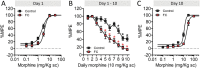
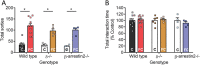
Exposure to severely stressful events during childhood is associated with poor health outcomes in later life, including chronic pain and substance use disorder. However, the mediators and mechanisms are unclear. We investigated the impact of a well-characterized mouse model of early-life adversity, fragmented maternal care (FC) between postnatal day 2 and 9, on nociception, inflammatory hypersensitivity, and responses to morphine. Male and female mice exposed to FC exhibited prolonged basal thermal withdrawal latencies and decreased mechanical sensitivity. In addition, morphine had reduced potency in mice exposed to FC and their development of tolerance to morphine was accelerated. Quantitative PCR analysis in several brain regions and the spinal cords of juvenile and adult mice revealed an impact of FC on the expression of genes encoding opioid peptide precursors and their receptors. These changes included enhanced abundance of δ opioid receptor transcript in the spinal cord. Acute inflammatory hypersensitivity (induced by hind paw administration of complete Freund's adjuvant) was unaffected by exposure to FC. However, after an initial recovery of mechanical hypersensitivity, there was a reappearance in mice exposed to FC by day 15, which was not seen in control mice. Changes in nociception, morphine responses, and hypersensitivity associated with FC were apparent in males and females but were absent from mice lacking δ receptors or β-arrestin2. These findings suggest that exposure to early-life adversity in mice enhances δ receptor expression leading to decreased basal sensitivity to noxious stimuli coupled with accelerated morphine tolerance and enhanced vulnerability to persistent inflammatory hypersensitivity.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Bohn LM, Gainetdinov RR, Lin FT, Lefkowitz RJ, Caron MG. μ-Opioid receptor desensitization by β-arrestin-2 determines morphine tolerance but not dependence. Nature 2000;408:720–3. - PubMed
-
- Burke NN, Finn DP, McGuire BE, Roche M. Psychological stress in early life as a predisposing factor for the development of chronic pain: clinical and preclinical evidence and neurobiological mechanisms. J Neurosci Res 2017;95:1257–70. - PubMed
-
- Busse JW, Wang L, Kamaleldin M, Craigie S, Riva JJ, Montoya L, Mulla SM, Lopes LC, Vogel N, Chen E, Kirmayr K, De Oliveira K, Olivieri L, Kaushal A, Chaparro LE, Oyberman I, Agarwal A, Couban R, Tsoi L, Lam T, Vandvik PO, Hsu S, Bala MM, Schandelmaier S, Scheidecker A, Ebrahim S, Ashoorion V, Rehman Y, Hong PJ, Ross S, Johnston BC, Kunz R, Sun X, Buckley N, Sessler DI, Guyatt GH. Opioids for chronic noncancer pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2018;320:2448–60. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

