Genetically proxied glucose-lowering drug target perturbation and risk of cancer: a Mendelian randomisation analysis
- PMID: 37171501
- PMCID: PMC10317892
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-023-05925-4
Genetically proxied glucose-lowering drug target perturbation and risk of cancer: a Mendelian randomisation analysis
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Epidemiological studies have generated conflicting findings on the relationship between glucose-lowering medication use and cancer risk. Naturally occurring variation in genes encoding glucose-lowering drug targets can be used to investigate the effect of their pharmacological perturbation on cancer risk.
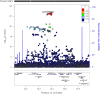
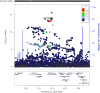
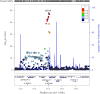
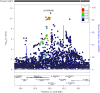
Methods: We developed genetic instruments for three glucose-lowering drug targets (peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ [PPARG]; sulfonylurea receptor 1 [ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 8 (ABCC8)]; glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor [GLP1R]) using summary genetic association data from a genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in 148,726 cases and 965,732 controls in the Million Veteran Program. Genetic instruments were constructed using cis-acting genome-wide significant (p<5×10-8) SNPs permitted to be in weak linkage disequilibrium (r2<0.20). Summary genetic association estimates for these SNPs were obtained from genome-wide association study (GWAS) consortia for the following cancers: breast (122,977 cases, 105,974 controls); colorectal (58,221 cases, 67,694 controls); prostate (79,148 cases, 61,106 controls); and overall (i.e. site-combined) cancer (27,483 cases, 372,016 controls). Inverse-variance weighted random-effects models adjusting for linkage disequilibrium were employed to estimate causal associations between genetically proxied drug target perturbation and cancer risk. Co-localisation analysis was employed to examine robustness of findings to violations of Mendelian randomisation (MR) assumptions. A Bonferroni correction was employed as a heuristic to define associations from MR analyses as 'strong' and 'weak' evidence.
Results: In MR analysis, genetically proxied PPARG perturbation was weakly associated with higher risk of prostate cancer (for PPARG perturbation equivalent to a 1 unit decrease in inverse rank normal transformed HbA1c: OR 1.75 [95% CI 1.07, 2.85], p=0.02). In histological subtype-stratified analyses, genetically proxied PPARG perturbation was weakly associated with lower risk of oestrogen receptor-positive breast cancer (OR 0.57 [95% CI 0.38, 0.85], p=6.45×10-3). In co-localisation analysis, however, there was little evidence of shared causal variants for type 2 diabetes liability and cancer endpoints in the PPARG locus, although these analyses were likely underpowered. There was little evidence to support associations between genetically proxied PPARG perturbation and colorectal or overall cancer risk or between genetically proxied ABCC8 or GLP1R perturbation with risk across cancer endpoints.
Conclusions/interpretation: Our drug target MR analyses did not find consistent evidence to support an association of genetically proxied PPARG, ABCC8 or GLP1R perturbation with breast, colorectal, prostate or overall cancer risk. Further evaluation of these drug targets using alternative molecular epidemiological approaches may help to further corroborate the findings presented in this analysis.
Data availability: Summary genetic association data for select cancer endpoints were obtained from the public domain: breast cancer ( https://bcac.ccge.medschl.cam.ac.uk/bcacdata/ ); and overall prostate cancer ( http://practical.icr.ac.uk/blog/ ). Summary genetic association data for colorectal cancer can be accessed by contacting GECCO (kafdem at fredhutch.org). Summary genetic association data on advanced prostate cancer can be accessed by contacting PRACTICAL (practical at icr.ac.uk). Summary genetic association data on type 2 diabetes from Vujkovic et al (Nat Genet, 2020) can be accessed through dbGAP under accession number phs001672.v3.p1 (pha004945.1 refers to the European-specific summary statistics). UK Biobank data can be accessed by registering with UK Biobank and completing the registration form in the Access Management System (AMS) ( https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/enable-your-research/apply-for-access ).
Keywords: ABCC8; Breast cancer; Colorectal cancer; GLP1R; Glucose-lowering drug targets; Mendelian randomisation; PPARG; Prostate cancer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA059045/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA154337/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA201407/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA122839/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 28534/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 DK134575/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018033/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA153323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M012190/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 CA086308/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 DK126194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 29017/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- S10 OD028685/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114347/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA074794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA137088/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076366/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207371/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261201700006I/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA191312/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003362/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 CA164930/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA206110/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U58 DP002333/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- R01 CA097325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K05 CA152715/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- 29019/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA081488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA015704/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

