RE-MIND2: comparative effectiveness of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide versus polatuzumab vedotin/bendamustine/rituximab (pola-BR), CAR-T therapies, and lenalidomide/rituximab (R2) based on real-world data in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 37171597
- PMCID: PMC10261238
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-023-05196-4
RE-MIND2: comparative effectiveness of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide versus polatuzumab vedotin/bendamustine/rituximab (pola-BR), CAR-T therapies, and lenalidomide/rituximab (R2) based on real-world data in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Erratum in
-
Correction to: RE‑MIND2: comparative effectiveness of tafasitamab plus lenalidomide versus polatuzumab vedotin/bendamustine/rituximab (pola‑BR), CAR‑T therapies, and lenalidomide/rituximab (R2) based on real‑world data in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B‑cell lymphoma.Ann Hematol. 2023 Sep;102(9):2643-2644. doi: 10.1007/s00277-023-05321-3. Ann Hematol. 2023. PMID: 37432417 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
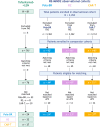
RE-MIND2 (NCT04697160) compared patient outcomes from the L-MIND (NCT02399085) trial of tafasitamab+lenalidomide with those of patients treated with other therapies for relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who are autologous stem cell transplant ineligible. We present outcomes data for three pre-specified treatments not assessed in the primary analysis. Data were retrospectively collected from sites in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific region. Patients were aged ≥18 years with histologically confirmed DLBCL and received ≥2 systemic therapies for DLBCL (including ≥1 anti-CD20 therapy). Patients enrolled in the observational and L-MIND cohorts were matched using propensity score-based 1:1 nearest-neighbor matching, balanced for six covariates. Tafasitamab+lenalidomide was compared with polatuzumab vedotin+bendamustine+rituximab (pola-BR), rituximab+lenalidomide (R2), and CD19-chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapies. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Secondary endpoints included treatment response and progression-free survival. From 200 sites, 3,454 patients were enrolled in the observational cohort. Strictly matched patient pairs consisted of tafasitamab+lenalidomide versus pola-BR (n = 24 pairs), versus R2 (n = 33 pairs), and versus CAR-T therapies (n = 37 pairs). A significant OS benefit was observed with tafasitamab+lenalidomide versus pola-BR (HR: 0.441; p = 0.034) and R2 (HR: 0.435; p = 0.012). Comparable OS was observed in tafasitamab+lenalidomide and CAR-T cohorts (HR: 0.953, p = 0.892). Tafasitamab+lenalidomide appeared to improve survival outcomes versus pola-BR and R2, and comparable outcomes were observed versus CAR-T. Although based on limited patient numbers, these data may help to contextualize emerging therapies for R/R DLBCL. CLINICAL TRIAL REGISTRATION: NCT04697160 (January 6, 2021).
Keywords: DLBCL; Lenalidomide; Real-world; Relapsed/Refractory; Tafasitamab.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Duell J, Maddocks KJ, González-Barca E, et al. Long-term outcomes from the Phase II L-MIND study of tafasitamab (MOR208) plus lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2021;106:2417–2426. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2020.275958. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- US Food & Drug Administration (2020) FDA grants accelerated approval to tafasitamab-cxix for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-approvals-and-databases/fda-grants-accele.... Accessed 23 Nov 2021
-
- European Medicines Agency (2021) Tafasitamab Summary of Opinion: Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop-initial/chmp-summary-positiv.... Accessed 27 Jul 2021
-
- Government of Canada, Health Canada, Public Affairs C and RB (2021) Drug Product Database: Minjuivi. https://health-products.canada.ca/dpd-bdpp/info.do?lang=en&code=100793. Accessed 21 Sep 2021
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

