Budget impact of endovascular treatment for acute ischaemic stroke patients in the Netherlands for 2015-2021
- PMID: 37171711
- PMCID: PMC10188812
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-023-01788-x
Budget impact of endovascular treatment for acute ischaemic stroke patients in the Netherlands for 2015-2021
Abstract
Introduction: Endovascular treatment (EVT) has been proven to be both effective and cost-effective for patients with acute ischaemic stroke. We investigated the budget impact of large-scale implementation of EVT for acute ischaemic stroke patients in the Netherlands for 2015-2021.
Methods: An analysis was performed from a healthcare perspective as a preplanned substudy of the Multicenter Randomized Clinical trial of Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke in the Netherlands (MR CLEAN). Estimated yearly costs during follow-up after stroke for patients who had or had not been treated with EVT as add-on to usual care were linked to numbers of new patients retrieved from 2 Dutch registries of EVT that started after the last inclusion in MR CLEAN (2014). Aggregated costs and costs per care sector were calculated based on prevalence using a population dynamic tool.
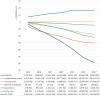
Results: From 2015, the yearly number of new acute ischaemic stroke patients receiving EVT increased almost threefold, from 812 in 2015 to 2,370 in 2021. The introduction of EVT plus usual care resulted in estimated net annual savings that increased from € 2.9 million in 2015 to € 58 million in 2021.
Conclusion: Offering EVT as add-on to usual care for acute ischaemic stroke patients was increasingly cost saving from a national healthcare perspective but affected distinct healthcare sectors differently.
Keywords: Economic Evaluation; Endovascular Procedures; Ischaemic Stroke; Thrombectomy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Erasmus Medical Centre received consulting fees from Stryker for A. van der Lugt. Maastricht University Medical Centre received consulting fees from Stryker and Cerenovus for W.H. van Zwam. C.B.L. Majoie received research grants from CVON/Dutch Heart Foundation, European Commission, Healthcare Evaluation Netherlands, TWIN Foundation and Stryker. C.B.L. Majoie and Y.B. Roos are shareholders of Nicolab, a company that focuses on the use of artificial intelligence for medical image analysis. D.W.J. Dippel and A. van der Lugt received grants from Stryker, Penumbra Inc., Medtronic, Cerenovus, Dutch Heart Foundation, Brain Foundation Netherlands, Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development and Thrombolytic Science, all unrestricted and paid to Erasmus Medical Centre. L.A. van den Berg, O.A. Berkhemer, P.S.S. Fransen, D. Beumer, R.J. van Oostenbrugge and M.G.W. Dijkgraaf declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Saqqur M, Uchino K, Demchuk AM, Molina CA, Garami Z, Calleja S, et al. Site of arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke. 2007;38:948–954. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000257304.21967.ba. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

