Revisiting MMPBSA by Adoption of MC-Based Surface Area/Volume, ANI-ML Potentials, and Two-Valued Interior Dielectric Constant
- PMID: 37171911
- PMCID: PMC10226125
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c00834
Revisiting MMPBSA by Adoption of MC-Based Surface Area/Volume, ANI-ML Potentials, and Two-Valued Interior Dielectric Constant
Abstract
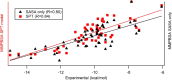
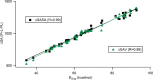
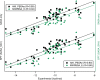
Here, we report the accuracy improvements of molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area (MMPBSA) calculations by adoption of ANI-ML potentials in replacement of MM terms, the use of solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) and volume (SAV) values from the Monte Carlo sampling of the probe, and introducing two different interior dielectric constants for electrostatic interactions of protein-ligand (P-L) and polar solvation term in the MMPBSA calculations. Our results show that the Pearson correlation coefficients of MMPBSA-calculated values with respect to experimental binding free energies can be drastically improved from 0.48 to 0.90 by adoption of ANI-ML potentials in replacement of MM energy terms in the equation, referred to as ANI-PBSA. Moreover, we show that the SASA/SAV-combined equation in the scaled particle theory (SPT) can be a better choice to model nonpolar solvation term, reaching nearly the same accuracy by ANI-PBSA calculations. Finally, we introduce two different values of interior dielectric constants, which could be an alternative strategy between the single and variable constant definitions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
g_mmpbsa--a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations.J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Jul 28;54(7):1951-62. doi: 10.1021/ci500020m. Epub 2014 Jun 19. J Chem Inf Model. 2014. PMID: 24850022
-
Statistical Analysis on the Performance of Molecular Mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann Surface Area versus Absolute Binding Free Energy Calculations: Bromodomains as a Case Study.J Chem Inf Model. 2017 Sep 25;57(9):2203-2221. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.7b00347. Epub 2017 Aug 24. J Chem Inf Model. 2017. PMID: 28786670 Free PMC article.
-
Calculating protein-ligand binding affinities with MMPBSA: Method and error analysis.J Comput Chem. 2016 Oct 15;37(27):2436-46. doi: 10.1002/jcc.24467. Epub 2016 Aug 11. J Comput Chem. 2016. PMID: 27510546 Free PMC article.
-
Development and test of highly accurate endpoint free energy methods. 1: Evaluation of ABCG2 charge model on solvation free energy prediction and optimization of atom radii suitable for more accurate solvation free energy prediction by the PBSA method.J Comput Chem. 2023 May 30;44(14):1334-1346. doi: 10.1002/jcc.27089. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Comput Chem. 2023. PMID: 36807356 Review.
-
Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jan 10;4:87. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00087. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29367919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DeepConf: Leveraging ANI-ML Potentials for Exploring Local Minima with Application to Bioactive Conformations.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Mar 24;65(6):2818-2833. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c02053. Epub 2025 Mar 3. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 40033575 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the polyspecificity of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase for non-canonical amino acids using molecular dynamics simulation and MM/PBSA.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 10;20(1):e0316907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316907. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39792834 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking ANI potentials as a rescoring function and screening FDA drugs for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2024 Mar 27;38(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10822-024-00554-4. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2024. PMID: 38532176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vangunsteren W. F.; Berendsen H. J. C. Computer-Simulation of Molecular-Dynamics - Methodology, Applications, and Perspectives in Chemistry. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1990, 29, 992.10.1002/anie.199009921. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

