Micrometeoroid infall onto Saturn's rings constrains their age to no more than a few hundred million years
- PMID: 37172091
- PMCID: PMC10181170
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adf8537
Micrometeoroid infall onto Saturn's rings constrains their age to no more than a few hundred million years
Abstract
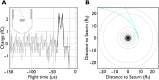
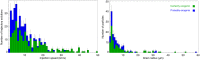
There is ongoing debate as to whether Saturn's main rings are relatively young or ancient- having been formed shortly after Saturn or during the Late Heavy Bombardment. The rings are mostly water-ice but are polluted by non-icy material with a volume fraction ranging from ∼0.1 to 2%. Continuous bombardment by micrometeoroids exogenic to the Saturnian system is a source of this non-icy material. Knowledge of the incoming mass flux of these pollutants allows estimation of the rings' exposure time, providing a limit on their age. Here we report the final measurements by Cassini's Cosmic Dust Analyzer of the micrometeoroid flux into the Saturnian system. Several populations are present, but the flux is dominated by low-relative velocity objects such as from the Kuiper belt. We find a mass flux between 6.9 · 10-17 and 2.7 · 10-16 kg m-2s-1 from which we infer a ring exposure time ≲100 to 400 million years in support of recent ring formation scenarios.
Figures
References
-
- Esposito L. W., O’callaghan M., West R. A., The structure of Saturn’s rings–Implications from the Voyager stellar occultation. Icarus 56, 439–452 (1983).
-
- Iess L., Militzer B., Kaspi Y., Nicholson P., Durante D., Racioppa P., Anabtawi A., Galanti E., Hubbard W., Mariani M. J., Tortora P., Wahl S., Zannoni M., Measurement and implications of Saturn’s gravity field and ring mass. Science 364, eaat2965 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Cuzzi J. N., Estrada P. R., Compositional evolution of saturn’s rings due to meteoroid bombardment. Icarus 132, 1–35 (1998).
-
- Durisen R. H., Bode P. W., Cuzzi J. N., Cederbloom S. E., Murphy B. W., Ballistic transport in planetary ring systems due to particle erosion mechanisms: II. Theoretical models for Saturn’s A- and B-ring inner edges. Icarus 100, 364–393 (1992).
-
- Auer S., Grün E., Srama R., Kempf S., Auer R., The charge and velocity detector of the cosmic dust analyzer on Cassini. Planet. Space Sci. 50, 773–779 (2002).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

