Paralog-specific signaling by IRAK1/4 maintains MyD88-independent functions in MDS/AML
- PMID: 37172199
- PMCID: PMC10517216
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018718
Paralog-specific signaling by IRAK1/4 maintains MyD88-independent functions in MDS/AML
Abstract
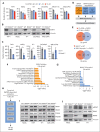
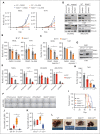
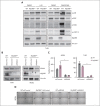
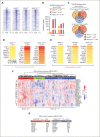
Dysregulation of innate immune signaling is a hallmark of hematologic malignancies. Recent therapeutic efforts to subvert aberrant innate immune signaling in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have focused on the kinase IRAK4. IRAK4 inhibitors have achieved promising, though moderate, responses in preclinical studies and clinical trials for MDS and AML. The reasons underlying the limited responses to IRAK4 inhibitors remain unknown. In this study, we reveal that inhibiting IRAK4 in leukemic cells elicits functional complementation and compensation by its paralog, IRAK1. Using genetic approaches, we demonstrate that cotargeting IRAK1 and IRAK4 is required to suppress leukemic stem/progenitor cell (LSPC) function and induce differentiation in cell lines and patient-derived cells. Although IRAK1 and IRAK4 are presumed to function primarily downstream of the proximal adapter MyD88, we found that complementary and compensatory IRAK1 and IRAK4 dependencies in MDS/AML occur via noncanonical MyD88-independent pathways. Genomic and proteomic analyses revealed that IRAK1 and IRAK4 preserve the undifferentiated state of MDS/AML LSPCs by coordinating a network of pathways, including ones that converge on the polycomb repressive complex 2 complex and JAK-STAT signaling. To translate these findings, we implemented a structure-based design of a potent and selective dual IRAK1 and IRAK4 inhibitor KME-2780. MDS/AML cell lines and patient-derived samples showed significant suppression of LSPCs in xenograft and in vitro studies when treated with KME-2780 as compared with selective IRAK4 inhibitors. Our results provide a mechanistic basis and rationale for cotargeting IRAK1 and IRAK4 for the treatment of cancers, including MDS/AML.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: D.T.S. serves on the scientific advisory board at Kurome Therapeutics; is a consultant for and/or received funding from Kurome Therapeutics, Captor Therapeutics, Treeline Biosciences, and Tolero Therapeutics; and has equity in Kurome Therapeutics. L.C.B. consulted for Kurome Therapeutics. J.R. is employed by, and holds equity in, Kurome Therapeutics; holds equity in Airway Therapeutics; and is a consultant for Radius Health and MoglingBio. A.K. is employed by, and holds equity in, Kurome Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures









Comment in
-
Double trouble: IRAK1/4 inhibitors in AML/MDS.Blood. 2023 Sep 14;142(11):945-946. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023020812. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37707874 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

