Serum fatty acid profiles in breast cancer patients following treatment
- PMID: 37173619
- PMCID: PMC10176817
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-023-10914-2
Serum fatty acid profiles in breast cancer patients following treatment
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is associated with alterations in lipid metabolism. The treatment of breast cancer can also affect serum lipid composition. The purpose of this study was the examination of serum fatty acids (FAs) profiles in breast cancer survivors to assess if the FA levels normalize.
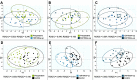
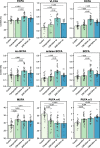
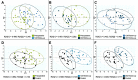
Methods: Serum levels of FAs were determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in a group of breast cancer patients at baseline (before treatment, n = 28), at two follow-up visits at 12 months (n = 27) and 24 months (n = 19) after the breast cancer resection, and in the group of healthy controls (n = 25). Multivariate analysis was performed to assess how FA serum profile changes following treatment.
Results: Breast cancer patients' serum FA profiles at follow-ups did not normalize to the levels of control group. The greatest differences were found for levels of branched-chain (BCFA), odd-chain (OCFA) and polyunsaturated (PUFAs) FAs, all of which were significantly increased 12 months after the surgery.
Conclusions: After treatment for breast cancer, the patients' serum FA profile differs from the profile before treatment and from controls, especially 12 months after treatment. Some changes may be beneficial - increased BCFA and OCFA levels, and improved n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio. This may reflect lifestyle changes in breast cancer survivors and have an impact on the risk of recurrence.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Fatty acids; Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; Lipids; Serum.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;0(0):caac.21660. - PubMed
-
- Hendrick RE, Baker JA, Helvie MA. Breast cancer deaths averted over 3 decades. Cancer. 2019;125(9):1482–8. 10.1002/cncr.31954. [cited 2022 Feb 28] - PubMed
-
- Ng HS, Vitry A, Koczwara B, Roder D, McBride ML. Patterns of comorbidities in women with breast cancer: a Canadian population-based study. Cancer Causes Control. 2019;30(9):931–41. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31280456/. [cited 2022 Mar 1] - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

