Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37173876
- PMCID: PMC10177524
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15092410
Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
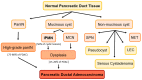
Pancreatic cancer is projected to become the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality in the United States by 2030. This is in part due to the paucity of reliable screening and diagnostic options for early detection. Amongst known pre-malignant pancreatic lesions, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are the most prevalent. The current standard of care for the diagnosis and classification of pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) involves cross-sectional imaging studies and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and, when indicated, EUS-guided fine needle aspiration and cyst fluid analysis. However, this is suboptimal for the identification and risk stratification of PCLs, with accuracy of only 65-75% for detecting mucinous PCLs. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a promising tool that has been applied to improve accuracy in screening for solid tumors, including breast, lung, cervical, and colon cancer. More recently, it has shown promise in diagnosing pancreatic cancer by identifying high-risk populations, risk-stratifying premalignant lesions, and predicting the progression of IPMNs to adenocarcinoma. This review summarizes the available literature on artificial intelligence in the screening and prognostication of precancerous lesions in the pancreas, and streamlining the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: IPMN; artificial intelligence; endoscopy; pancreatic cysts; pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving Pancreatic Cyst Management: Artificial Intelligence-Powered Prediction of Advanced Neoplasms through Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Confocal Endomicroscopy.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;8(6):496. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8060496. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy and agreement of a large panel of endosonographers for endomicroscopy-guided virtual biopsy of pancreatic cystic lesions.Pancreatology. 2022 Nov;22(7):994-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2022.08.012. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Pancreatology. 2022. PMID: 36089484 Free PMC article.
-
EUS is accurate in characterizing pancreatic cystic lesions; a prospective comparison with cross-sectional imaging in resected cases.Surg Endosc. 2021 Dec;35(12):6650-6659. doi: 10.1007/s00464-020-08166-3. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Surg Endosc. 2021. PMID: 33259018 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Needle-Based Confocal Endomicroscopy as a Diagnostic Imaging Biomarker for Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;16(6):1238. doi: 10.3390/cancers16061238. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38539568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the diagnostic evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Feb 14;28(6):624-634. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i6.624. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35317424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Basic Principles and Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Diagnosis and Differentiation of Pancreatic Cancer from Other Pancreatic Lesions: A Comprehensive Review of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Cancer.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 28;13(9):2599. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092599. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38731128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of artificial intelligence in EUS.Endosc Ultrasound. 2024 Mar-Apr;13(2):65-75. doi: 10.1097/eus.0000000000000053. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Endosc Ultrasound. 2024. PMID: 38947752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of landscape exploration and progress in molecular therapies and precision medicine for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):103337. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.103337. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40697241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Imaging Modalities and the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Analyzing CT and MRI Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 16;14(4):438. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040438. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances for Managing Pancreatic Cystic Lesions: Integrating Imaging and AI Innovations.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 22;16(24):4268. doi: 10.3390/cancers16244268. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sagami R., Sato T., Mizukami K., Motomura M., Okamoto K., Fukuchi S., Otsuka Y., Abe T., Ono H., Mori K., et al. Diagnostic Strategy of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer via Clinical Predictor Assessment: Clinical Indicators, Risk Factors and Imaging Findings. Diagnostics. 2022;12:377. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020377. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

