Superinfection of Rectovaginal Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 37174906
- PMCID: PMC10177285
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091514
Superinfection of Rectovaginal Endometriosis: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background: A peculiar complication of endometriosis is a superinfection. However, the superinfection of extra-ovarian endometriosis is anecdotal, and only a few cases have been described. We wanted to present the first cases of the superinfection of rectovaginal endometriosis and to perform a literature review of the superinfection of extra-ovarian endometriosis.
Methods: We present a case of a 24-year-old woman who was referred to our Pelvic Floor Unit for rectal-perineal pain, dyspareunia, and recurrent episodes of dense purulent vaginal discharge for one year, in which the superinfection of rectovaginal endometriosis was diagnosed. Moreover, we performed a systematic search of the literature indexed on PubMed up to 31 January 2023.
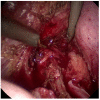
Results: Laparoscopic drainage was successful in managing this condition. In the literature, clinical presentation and instrumental and microbiological findings are very heterogeneous. However, the gold standard of management is represented by surgical or percutaneous drainage.
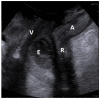
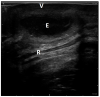
Conclusions: In the case of a pelvic abscess, the superinfection of endometriosis lesions should be suspected, and this can represent the onset symptom of endometriosis. Ultrasonography may show nodular or flat hypoechoic lesions with hyperechoic debris and peripheral positive color/power Doppler intensities. The goal of management is to drain the abscess, either percutaneously or via traditional surgery, followed by proper hormonal therapy to reduce recurrence.
Keywords: chronic pelvic pain; endometriosis; laparoscopy; pelvic floor ultrasound; rectovaginal space; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Taylor H.S., Fritz M.A., Pal L., Seli E. Speroff’s Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility. 9th ed. Wolters Kluwer; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

