OView-AI Supporter for Classifying Pneumonia, Pneumothorax, Tuberculosis, Lung Cancer Chest X-ray Images Using Multi-Stage Superpixels Classification
- PMID: 37174910
- PMCID: PMC10177540
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091519
OView-AI Supporter for Classifying Pneumonia, Pneumothorax, Tuberculosis, Lung Cancer Chest X-ray Images Using Multi-Stage Superpixels Classification
Abstract
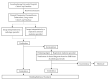
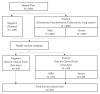
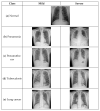
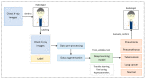
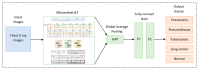
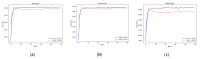
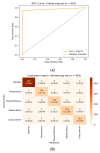
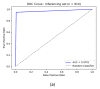
The deep learning approach has recently attracted much attention for its outstanding performance to assist in clinical diagnostic tasks, notably in computer-aided solutions. Computer-aided solutions are being developed using chest radiography to identify lung diseases. A chest X-ray image is one of the most often utilized diagnostic imaging modalities in computer-aided solutions since it produces non-invasive standard-of-care data. However, the accurate identification of a specific illness in chest X-ray images still poses a challenge due to their high inter-class similarities and low intra-class variant abnormalities, especially given the complex nature of radiographs and the complex anatomy of the chest. In this paper, we proposed a deep-learning-based solution to classify four lung diseases (pneumonia, pneumothorax, tuberculosis, and lung cancer) and healthy lungs using chest X-ray images. In order to achieve a high performance, the EfficientNet B7 model with the pre-trained weights of ImageNet trained by Noisy Student was used as a backbone model, followed by our proposed fine-tuned layers and hyperparameters. Our study achieved an average test accuracy of 97.42%, sensitivity of 95.93%, and specificity of 99.05%. Additionally, our findings were utilized as diagnostic supporting software in OView-AI system (computer-aided application). We conducted 910 clinical trials and achieved an AUC confidence interval (95% CI) of the diagnostic results in the OView-AI system of 97.01%, sensitivity of 95.68%, and specificity of 99.34%.
Keywords: EfficientNet; deep learning; lung cancer; pneumonia; pneumothorax; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AI-CenterNet CXR: An artificial intelligence (AI) enabled system for localization and classification of chest X-ray disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 30;9:955765. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.955765. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36111113 Free PMC article.
-
Observer Performance Evaluation of a Deep Learning Model for Multilabel Classification of Active Tuberculosis Lung Zone-Wise Manifestations.Cureus. 2023 Sep 9;15(9):e44954. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44954. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37818499 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning in Multi-Class Lung Diseases' Classification on Chest X-ray Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 6;12(4):915. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040915. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453963 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub4. PMID: 33242342 Updated.
-
Artificial Intelligence Solutions for Analysis of X-ray Images.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021 Feb;72(1):60-72. doi: 10.1177/0846537120941671. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021. PMID: 32757950 Review.
Cited by
-
Active and Inactive Tuberculosis Classification Using Convolutional Neural Networks with MLP-Mixer.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jun 9;12(6):630. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12060630. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564446 Free PMC article.
-
Four Transformer-Based Deep Learning Classifiers Embedded with an Attention U-Net-Based Lung Segmenter and Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation-Based Heatmaps for COVID-19 X-ray Scans.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(14):1534. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14141534. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lung Diseases National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. [(accessed on 28 November 2022)]; Available online: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/conditions/lung-disease/index.cfm.
-
- Dodia S., Aannappa B., Mahesh P.A. Recent Advancements in Deep Learning based Lung Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022;116:105490. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105490. - DOI
-
- Pneumonia System and Diagnosis American Lung Association. [(accessed on 28 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/pneumonia/....
-
- Tuberculosis System and Diagnosis American Lung Association. [(accessed on 28 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/tuberculos....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

