A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing the Diagnostic Accuracy Tests of COVID-19
- PMID: 37174941
- PMCID: PMC10177430
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091549
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Comparing the Diagnostic Accuracy Tests of COVID-19
Abstract
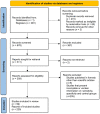
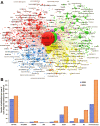
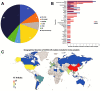
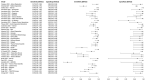
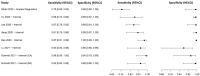
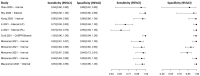
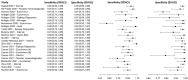
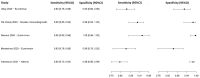
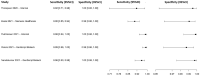
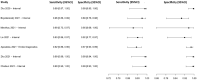
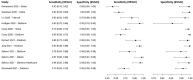
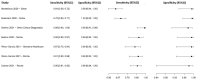
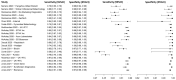
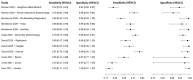
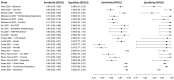
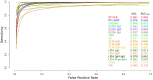
In this paper, we present a systematic review and meta-analysis that aims to evaluate the reliability of coronavirus disease diagnostic tests in 2019 (COVID-19). This article seeks to describe the scientific discoveries made because of diagnostic tests conducted in recent years during the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. Between 2020 and 2021, searches for published papers on the COVID-19 diagnostic were made in the PubMed database. Ninety-nine scientific articles that satisfied the requirements were analyzed and included in the meta-analysis, and the specificity and sensitivity of the diagnostic accuracy were assessed. When compared to serological tests such as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA), lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA), and chemiluminescent microparticle immunoassay (CMIA), molecular tests such as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) performed better in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Additionally, the area under the curve restricted to the false-positive rates (AUCFPR) of 0.984 obtained by the antiviral neutralization bioassay (ANB) diagnostic test revealed significant potential for the identification of COVID-19. It has been established that the various diagnostic tests have been effectively adapted for the detection of SARS-CoV-2; nevertheless, their performance still must be enhanced to contain potential COVID-19 outbreaks, which will also help contain potential infectious agent outbreaks in the future.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; diagnostic tests; meta-analysis; sensitivity; specificity; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 13 February 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

