Giant Tumefactive Perivascular Space: Advanced Fusion MR Imaging and Tractography Study-A Case Report and a Systematic Review
- PMID: 37174993
- PMCID: PMC10177987
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091602
Giant Tumefactive Perivascular Space: Advanced Fusion MR Imaging and Tractography Study-A Case Report and a Systematic Review
Abstract
Perivascular spaces (PVSs) are small extensions of the subpial cerebrospinal space, pial-lined and interstitial fluid-filled. They surround small penetrating arteries, and veins, crossing the subarachnoid space to the brain tissue. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) shows a PVS as a round-shape or linear structure, isointense to the cerebrospinal fluid, and, if larger than 1.5 cm, they are known as giant/tumefactive PVSs (GTPVS) that may compress neighboring parenchymal/liquoral compartment. We report a rare asymptomatic case of GTPVS type 1 in a diabetic middle-aged patient, occasionally discovered. Our MRI study focuses on diffusion/tractography and fusion imaging: three-dimensional (3D) constructive interference in steady state (CISS) and time of fly (TOF) sequences. The advanced and fusion MR techniques help us to track brain fiber to assess brain tissue compression consequences and some PVS anatomic features as the perforating arteries inside them.
Keywords: advanced magnetic resonance; giant/tumefactive perivascular spaces; magnetic resonance; perivascular spaces.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
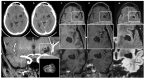
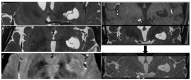


References
-
- Capasso R., Negro A., Cirillo S., Iovine S., Puoti G., Cirillo M., Conforti R. Large anterior temporal Virchow–Robin spaces: Evaluating MRI features over the years—Our experience and literature review. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2020;4:2514183X20905252. doi: 10.1177/2514183X20905252. - DOI
-
- Conforti R., Cirillo M., Sardaro A., Caiazzo G., Negro A., Paccone A., Sacco R., Sparaco M., Gallo A., Lavorgna L., et al. Dilated perivascular spaces and fatigue: Is there a link? Magnetic resonance retrospective 3Tesla study. Neuroradiology. 2016;58:859–866. doi: 10.1007/s00234-016-1711-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

