A Hybridized Machine Learning Approach for Predicting COVID-19 Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System and Reptile Search Algorithm
- PMID: 37175032
- PMCID: PMC10178244
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091641
A Hybridized Machine Learning Approach for Predicting COVID-19 Using Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System and Reptile Search Algorithm
Abstract
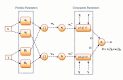
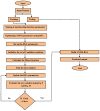
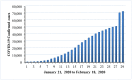
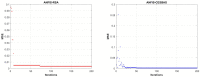
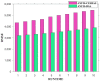
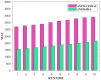
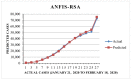
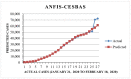
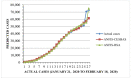
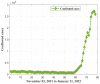
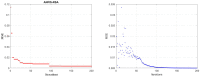
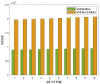
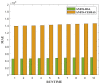
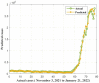
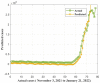
This research is aimed to escalate Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) functioning in order to ensure the veracity of existing time-series modeling. The COVID-19 pandemic has been a global threat for the past three years. Therefore, advanced forecasting of confirmed infection cases is extremely essential to alleviate the crisis brought out by COVID-19. An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-reptile search algorithm (ANFIS-RSA) is developed to effectively anticipate COVID-19 cases. The proposed model integrates a machine-learning model (ANFIS) with a nature-inspired Reptile Search Algorithm (RSA). The RSA technique is used to modulate the parameters in order to improve the ANFIS modeling. Since the performance of the ANFIS model is dependent on optimizing parameters, the statistics of infected cases in China and India were employed through data obtained from WHO reports. To ensure the accuracy of our estimations, corresponding error indicators such as RMSE, RMSRE, MAE, and MAPE were evaluated using the coefficient of determination (R2). The recommended approach employed on the China dataset was compared with other upgraded ANFIS methods to identify the best error metrics, resulting in an R2 value of 0.9775. ANFIS-CEBAS and Flower Pollination Algorithm and Salp Swarm Algorithm (FPASSA-ANFIS) attained values of 0.9645 and 0.9763, respectively. Furthermore, the ANFIS-RSA technique was used on the India dataset to examine its efficiency and acquired the best R2 value (0.98). Consequently, the suggested technique was found to be more beneficial for high-precision forecasting of COVID-19 on time-series data.
Keywords: COVID-19 influenza; coefficient of determination; fuzzy logic; nature-inspired algorithms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization Method for Forecasting Confirmed Cases of COVID-19 in China.J Clin Med. 2020 Mar 2;9(3):674. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030674. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32131537 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of the reptile search algorithm and the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system enhances standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index forecasting.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 26;15(1):14647. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98772-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40287468 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach.Sustain Cities Soc. 2021 Mar;66:102669. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102669. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Sustain Cities Soc. 2021. PMID: 33520607 Free PMC article.
-
Sensorless vector-controlled induction motor drives: Boosting performance with Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System integrated augmented Model Reference Adaptive System.MethodsX. 2024 Oct 5;13:102992. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2024.102992. eCollection 2024 Dec. MethodsX. 2024. PMID: 39676841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of machine learning in the prediction of COVID-19 daily new cases: A scoping review.Heliyon. 2021 Oct;7(10):e08143. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08143. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34660935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An intuitionistic fuzzy graph's variation coefficient measure with application to selecting a reliable alliance partner.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 3;14(1):18000. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68371-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39097655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamadneh N.N., Khan W.A., Ashraf W., Atawneh S.H., Khan I., Hamadneh B.N. Artificial neural networks for prediction of COVID-19 in Saudi Arabia. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021;66:2787–2796. doi: 10.32604/cmc.2021.013228. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

