Evaluation of Dental Root Development Regarding Maxillary Canine Eruption Status after Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate
- PMID: 37175033
- PMCID: PMC10178012
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091642
Evaluation of Dental Root Development Regarding Maxillary Canine Eruption Status after Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Patients with Cleft Lip and Palate
Abstract
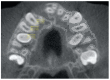
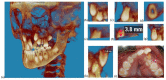
In children born with cleft lip and palate, the timing of the secondary alveolar bone graft (SABG) is crucial to its success; this involves estimating the eruption of the permanent maxillary canine. Altered dental eruption in this patient group gives impetus to the identification of dental developmental factors concerning maxillary canine eruption, which may steer the clinical decision of SABG timing. Records of over nine hundred patients who received SABG with pre- and post-operative cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans were analyzed for inclusion and divided into two groups (erupting or non-erupting canine after SABG). Roots of the maxillary canines and premolars were segmented from the cementoenamel junction then linear and volumetric measurements were performed. The pre- and post-operative root length and volume differences were calculated and compared statistically using independent sample tests and paired t-tests. No statistically significant differences were found in the volume change (%), or reciprocal of mean root length in the erupted and unerupted groups in the canine, first premolar, or second premolar roots except for an association between the post-operative dental root length of the canine and the maxillary canine eruption status. Therefore, assessment of root development from pre-treatment CBCT scans was not deemed worthy from a diagnostic perspective.
Keywords: cleft lip and palate; cone beam computer tomography (CBCT); maxillary canine eruption; secondary alveolar bone graft (SABG).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional evaluation of secondary alveolar bone grafting in patients with unilateral cleft lip and palate: A 2-3 year post-operative follow-up.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2024 Jun;27 Suppl 1:100-108. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12763. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2024. PMID: 38299981
-
Comparison of dental outcomes in patients with nonsyndromic complete unilateral cleft lip and palate who receive secondary alveolar bone grafting before or after emergence of the permanent maxillary canine.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020 May;157(5):668-679. doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2019.11.012. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2020. PMID: 32354440
-
Three-dimensional assessment of the eruption path of the canine in individuals with bone-grafted alveolar clefts using cone beam computed tomography.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2010 Sep;47(5):507-12. doi: 10.1597/08-171. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2010. PMID: 20184425
-
Optimal Timing of Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting: A Literature Review.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Apr;77(4):843-849. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.11.019. Epub 2018 Nov 26. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30576671 Review.
-
Long-Term Stability of Alveolar Bone Graft in Cleft Lip and Palate Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Craniofac Surg. 2022 Mar-Apr 01;33(2):e194-e200. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000008254. J Craniofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35385241
Cited by
-
Characterization and functional prediction of the dental plaque microbiome in patients with alveolar clefts.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 10;14:1361206. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1361206. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38800834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oberoi S., Gill P., Chigurupati R., Hoffman W.Y., Hatcher D.C., Vargervik K. Three-dimensional assessment of the eruption path of the canine in individuals with bone-grafted alveolar clefts using cone beam computed tomography. Cleft Palate Craniofac. J. 2010;47:507–512. doi: 10.1597/08-171. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salari N., Darvishi N., Heydari M., Bokaee S., Darvishi F., Mohammadi M. Global prevalence of cleft palate, cleft lip and cleft palate and lip: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022;123:110–120. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2021.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

