A Novel Deep Transfer Learning-Based Approach for Automated Pes Planus Diagnosis Using X-ray Image
- PMID: 37175053
- PMCID: PMC10178173
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13091662
A Novel Deep Transfer Learning-Based Approach for Automated Pes Planus Diagnosis Using X-ray Image
Abstract
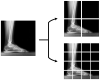
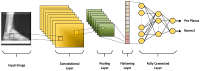
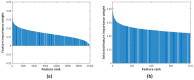
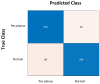
Pes planus, colloquially known as flatfoot, is a deformity defined as the collapse, flattening or loss of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. The first standard radiographic examination for diagnosing pes planus involves lateral and dorsoplantar weight-bearing radiographs. Recently, many artificial intelligence-based computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems and models have been developed for the detection of various diseases from radiological images. However, to the best of our knowledge, no model and system has been proposed in the literature for automated pes planus diagnosis using X-ray images. This study presents a novel deep learning-based model for automated pes planus diagnosis using X-ray images, a first in the literature. To perform this study, a new pes planus dataset consisting of weight-bearing X-ray images was collected and labeled by specialist radiologists. In the preprocessing stage, the number of X-ray images was augmented and then divided into 4 and 16 patches, respectively in a pyramidal fashion. Thus, a total of 21 images are obtained for each image, including 20 patches and one original image. These 21 images were then fed to the pre-trained MobileNetV2 and 21,000 features were extracted from the Logits layer. Among the extracted deep features, the most important 1312 features were selected using the proposed iterative ReliefF algorithm, and then classified with support vector machine (SVM). The proposed deep learning-based framework achieved 95.14% accuracy using 10-fold cross validation. The results demonstrate that our transfer learning-based model can be used as an auxiliary tool for diagnosing pes planus in clinical practice.
Keywords: X-ray image classification; deep learning; iterative ReliefF; pes planus; pyramidal feature extraction; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Utilization of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of pes planus and pes cavus with a smartphone camera.World J Orthop. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):1146-1154. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i12.1146. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39744730 Free PMC article.
-
A New Pes Planus Automatic Diagnosis Method: ViT-OELM Hybrid Modeling.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;15(7):867. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070867. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218217 Free PMC article.
-
Decision Tree-Based Foot Orthosis Prescription for Patients with Pes Planus.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Sep 30;19(19):12484. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912484. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36231782 Free PMC article.
-
The outcomes of subtalar arthroereisis in pes planus: a systemic review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021 May;141(5):761-773. doi: 10.1007/s00402-020-03458-8. Epub 2020 May 6. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021. PMID: 32377845
-
A Simplified Framework for the Detection of Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT Brain Images Using Deep Learning.Curr Med Imaging. 2021;17(10):1226-1236. doi: 10.2174/1573405617666210218100641. Curr Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33602101 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilization of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of pes planus and pes cavus with a smartphone camera.World J Orthop. 2024 Dec 18;15(12):1146-1154. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v15.i12.1146. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. World J Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39744730 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Model Based on CNN-ViT Fusion and Ensemble Learning for the Automatic Detection of Pes Planus.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 15;13(16):4800. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164800. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200942 Free PMC article.
-
A New Pes Planus Automatic Diagnosis Method: ViT-OELM Hybrid Modeling.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 28;15(7):867. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070867. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218217 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of calcaneal inclusion angle in the diagnosis of pes planus with pretrained deep learning networks: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Aug 1;104(31):e43639. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043639. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40760538 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Landmark Detection Model for Multiple Foot Deformity Classification: A Dual-Center Study.Yonsei Med J. 2025 Aug;66(8):491-501. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2024.0246. Yonsei Med J. 2025. PMID: 40709679 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

