Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Cysteine Modified Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots Based Sensor for Rapid Detection of Dopamine Hydrochloride
- PMID: 37175056
- PMCID: PMC10180347
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093646
Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Cysteine Modified Zinc Sulfide Quantum Dots Based Sensor for Rapid Detection of Dopamine Hydrochloride
Abstract
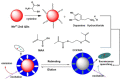
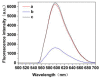
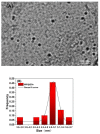
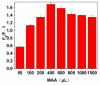
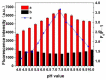
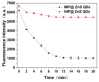
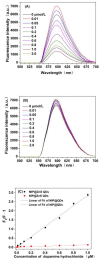
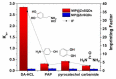
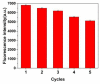
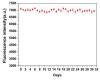
By combining surface molecular imprinting technology with cysteine-modified ZnS quantum dots, an elegant, molecularly imprinted cysteine-modified Mn2+: ZnS QDs (MIP@ZnS QDs) based fluorescence sensor was successfully developed. The constructed fluorescence sensor is based on a molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) coated on the surface cysteine-modified ZnS quantum dots and used for rapid fluorescence detection of dopamine hydrochloride. The MIP@ZnS quantum dots possess the advantages of rapid response, high sensitivity, and selectivity for the detection of dopamine hydrochloride molecules. Experimental results show that the adsorption equilibrium time of MIP@ZnS QDs for dopamine hydrochloride molecules is 12 min, and it can selectively capture and bind dopamine in the sample with an imprinting factor of 29.5. The fluorescence quenching of MIP@ZnS QDs has a good linear (R2 = 0.9936) with the concentration of dopamine hydrochloride ranged from 0.01 to 1.0 μM, and the limit of detection is 3.6 nM. In addition, The MIP@ZnS QDs demonstrate good recyclability and stability and are successfully employed for detection of dopamine hydrochloride in urine samples with recoveries was 95.2% to 103.8%. The proposed MIP@ZnS QDs based fluorescent sensor provides a promising approach for food safety detection and drug analysis.
Keywords: dopamine hydrochloride; fluorescent sensor; molecular imprinting; quantum dots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel fluorescent sensor for selective rifampicin detection based on the bio-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer-AgInS2/ZnS quantum dots.Anal Sci. 2024 Jun;40(6):1051-1059. doi: 10.1007/s44211-024-00512-y. Epub 2024 Mar 10. Anal Sci. 2024. PMID: 38461465
-
Molecular Imprinted ZnS Quantum Dots-Based Sensor for Selective Sulfanilamide Detection.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Aug 29;14(17):3540. doi: 10.3390/polym14173540. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36080615 Free PMC article.
-
A functional ratio fluorescence sensor platform based on the graphene/Mn-ZnS quantum dots loaded with molecularly imprinted polymer for selective and visual detection sinapic acid.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 Jan 5;244:118845. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118845. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 32882656
-
[Application of novel quantum dot-based molecularly imprinted fluorescence sensor in rapid detection].Se Pu. 2021 Aug;39(8):775-780. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.02025. Se Pu. 2021. PMID: 34212579 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Molecularly imprinted polymer grafted on paper and flat sheet for selective sensing and diagnosis: a review.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Jul 30;188(8):279. doi: 10.1007/s00604-021-04930-x. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 34331135 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and Application Progress of Imprinted Polymers.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 17;15(10):2344. doi: 10.3390/polym15102344. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent-Nanoparticle-Impregnated Nanocomposite Polymeric Gels for Biosensing and Drug Delivery Applications.Gels. 2023 Aug 18;9(8):669. doi: 10.3390/gels9080669. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37623124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xiao S., Sun L., Lu J., Dong Z. A label-free aptasensor for rapid detection of clenbuterol based on SYBR Green I. New J. Chem. 2022;46:16177–16182. doi: 10.1039/D2NJ01959K. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

