Evolution of the Electronic Structure of the trans-[Re6S8bipy4Cl2] Octahedral Rhenium Cluster during Reduction
- PMID: 37175068
- PMCID: PMC10180412
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093658
Evolution of the Electronic Structure of the trans-[Re6S8bipy4Cl2] Octahedral Rhenium Cluster during Reduction
Abstract
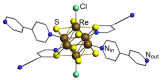
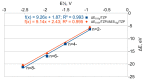
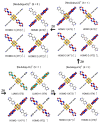
Understanding the processes that occur during the redox transformations of complexes coordinated by redox-active apical ligands is important for the design of electrochemically active compounds with functional properties. In this work, a detailed analysis of the interaction energy and electronic structure was performed for cluster complexes trans-[Re6S8bipy4Cl2]n (n = 2-, 4-, 6-, 8-), which can be obtained by stepwise electrochemical reduction of a neutral cluster trans-[Re6S8bipy4Cl2] in DMSO solution. It was shown that the formation of open-shell paramagnetic ions with S = 1, 2 and 1 is the most energetically favorable for n = 2-, 4- and 6-, respectively.
Keywords: DFT; ELF; cyclic voltammetry; octahedral rhenium clusters; reduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


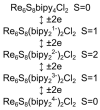
Similar articles
-
Soluble Molecular Rhenium Cluster Complexes Exhibiting Multistage Terminal Ligands Reduction.Inorg Chem. 2020 May 4;59(9):6460-6470. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c00546. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32319770
-
Octahedral Rhenium Cluster Complexes with 1,2-Bis(4-pyridyl)ethylene and 1,3-Bis(4-pyridyl)propane as Apical Ligands.Molecules. 2022 Nov 15;27(22):7874. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227874. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431984 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning the Ground- and Excited-State Redox Potentials of Octahedral Hexanuclear Rhenium(III) Complexes by the Combination of Terminal Halide and N-Heteroaromatic Ligands.ACS Omega. 2022 Jul 21;7(30):26965-26982. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03834. eCollection 2022 Aug 2. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35936475 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning of redox potentials for the design of ruthenium anticancer drugs -- an electrochemical study of [trans-RuCl(4)L(DMSO)](-) and [trans-RuCl(4)L(2)](-) complexes, where L = imidazole, 1,2,4-triazole, indazole.Inorg Chem. 2004 Nov 1;43(22):7083-93. doi: 10.1021/ic049479c. Inorg Chem. 2004. PMID: 15500346
-
Stabilization of Re37+/Re38+ Metalloclusters by Cyanide Ligands in New Trinuclear Rhenium Cluster Complexes [{Re3X3}(CN)9]4-/[{Re3X3}(CN)9]5- (X = Br or I).Inorg Chem. 2021 Apr 19;60(8):5980-5987. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00399. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33821642
References
-
- Shul’pin G.B., Kozlov Y.N., Shul’pina L.S. Metal Complexes Containing Redox-Active Ligands in Oxidation of Hydrocarbons and Alcohols: A Review. Catalysts. 2019;9:1046. doi: 10.3390/catal9121046. - DOI
-
- Lyaskovskyy V., de Bruin B. Redox Non-Innocent Ligands: Versatile New Tools to Control Catalytic Reactions. ACS Catal. 2012;2:270–279. doi: 10.1021/cs200660v. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

