Potential Effects of Geraniol on Cancer and Inflammation-Related Diseases: A Review of the Recent Research Findings
- PMID: 37175079
- PMCID: PMC10180430
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093669
Potential Effects of Geraniol on Cancer and Inflammation-Related Diseases: A Review of the Recent Research Findings
Abstract
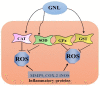
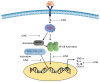
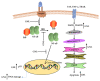
Geraniol (GNL), a natural monoterpene, is found in many essential oils of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, including lavender, citronella, lemongrass, and other medicinal and aromatic plants. GNL is commonly used by the cosmetic and food industries and has shown a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, antioxidant, and neuroprotective activities. It represents a potential anti-inflammatory agent and a promising cancer chemopreventive agent, as it has been found to be effective against a broad range of cancers, including colon, prostate, breast, lung, skin, kidney, liver, and pancreatic cancer. Moreover, GNL scavenges free radicals and preserves the activity of antioxidant enzymes. In addition, GNL induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, modulates multiple molecular targets, including p53 and STAT3, activates caspases, and modulates inflammation via transcriptional regulation. In the present study, different modes of action are described for GNL's activity against cancer and inflammatory diseases. This compound protects various antioxidant enzymes, such as catalase, glutathione-S-transferase, and glutathione peroxidase. Experiments using allergic encephalomyelitis, diabetes, asthma, and carcinogenesis models showed that GNL treatment had beneficial effects with low toxicity. GNL has been shown to be effective in animal models and tumor cell lines, but there have not been any clinical studies carried out for it. The aim of the present review is to provide updated data on the potential effects of GNL on cancer and inflammation, and to enhance our understanding of molecular targets, involved pathways, and the possible use of GNL for clinical studies and therapeutic purposes in the treatment of cancer and inflammation-related diseases.
Keywords: anticancer; antioxidant; chemo preventive effects; geraniol; inflammation diseases; molecular targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geraniol attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation-mediated cognitive impairment in D galactose-induced mouse aging model.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 20;16(6):5000-5026. doi: 10.18632/aging.205677. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38517361 Free PMC article.
-
One Hundred Faces of Geraniol.Molecules. 2020 Jul 21;25(14):3303. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143303. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32708169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective Impact of Geraniol Against CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats.Pak J Biol Sci. 2020 Jan;23(12):1650-1658. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2020.1650.1658. Pak J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33274899
-
Thymoquinone: potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 15;83(4):443-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.09.029. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22005518 Review.
-
Kaempferol, a potential cytostatic and cure for inflammatory disorders.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Oct 30;86:103-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.08.011. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25147152 Review.
Cited by
-
Linalool and Geraniol Defend Neurons from Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Iron Accumulation in In Vitro Parkinson's Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 29;13(8):917. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080917. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199163 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Hydrolysis Studies of a Prodrug Obtained as Ester Conjugate of Geraniol and Ferulic Acid by Enzymatic Way.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 6;25(11):6263. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116263. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892454 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD6 Autoantibodies as a Potential Biomarker for Inflammation-Related Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4935. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094935. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732153 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological potential of bioactive compounds in Catharanthus roseus extract: A comprehensive review.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Mar 17;14:101998. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101998. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40213418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting IDO1 in Huntington's Disease: Network Pharmacology and Preclinical Evidence from Coffea arabica.Neurochem Res. 2025 Aug 13;50(4):263. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04509-5. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40801953
References
-
- Hegde M.M., Lakshman K. Role of Polyphenols and Flavonoids as Anti-Cancer Drug Candidates: A Review. Pharmacognosy Res. 2023;15:206–216. doi: 10.5530/pres.15.2.022. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous