Polygonum orientale L. Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Induced Injury via Activation of MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 37175097
- PMCID: PMC10180121
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093687
Polygonum orientale L. Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Induced Injury via Activation of MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
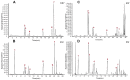
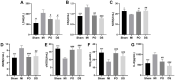
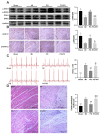
Although Polygonum orientale L. (PO) has a beneficial effect on treatment of myocardial ischemia (MI), its mechanism remains unclear. This study aimed to explore the pharmacological mechanism of PO against MI through MAPK signaling pathways. Firstly, the therapeutic effect of PO was evaluated for treatment of MI mice. Using Western blot and immunohistochemistry, the influence of PO on MAPK signaling pathways and cell apoptosis was investigated. Subsequently, one key pathway (ERK) of MAPK signaling pathways was screened out, on which PO posed the most obvious impact. Finally, an inhibitor of ERK1/2 was utilized to further verify the regulatory effect of PO on the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. It was found that PO could reduce the elevation of the ST segment; injury of heart tissue; the activity of LDH, CK, NOS, cNOS and iNOS and the levels of NO, BNP, TNF-α and IL-6. It is notable that PO could significantly modulate the protein content of p-ERK/ERK in mice suffering from MI but hardly had an effect on p-JNK/JNK and p-p38/p38. Additionally, the expressions of bax, caspase3 and caspase9 were inhibited in heart tissue in the PO-treated group. To evaluate whether ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059) could block the effect of PO on treatment of MI, both PO and PD98059 were given to mice with MI. It was discovered that the inhibitor indeed could significantly reverse the regulatory effects of PO on the above indicators, indicating that PO could regulate p-ERK/ERK. This study provides experimental evidence that PO extenuates MI injury, cardiomyocyte apoptosis and inflammation by activating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
Keywords: MAPK signaling pathway; Polygonum orientale L.; myocardial ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest in this study.
Figures




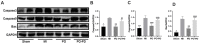
Similar articles
-
Exploring the Mechanisms of Polygonum orientale L. Against Myocardial Ischemia: An Integrated Analysis Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry, Network Pharmacology, and RNA Sequencing.Biomed Chromatogr. 2025 Jun;39(6):e70089. doi: 10.1002/bmc.70089. Biomed Chromatogr. 2025. PMID: 40255154
-
Lagopsis supina ameliorates myocardial ischemia injury by regulating angiogenesis, thrombosis, inflammation, and energy metabolism through VEGF, ROS and HMGB1 signaling pathways in rats.Phytomedicine. 2023 Nov;120:155050. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155050. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37708818
-
Sevoflurane Pre-conditioning Ameliorates Diabetic Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Via Differential Regulation of p38 and ERK.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 8;10(1):23. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56897-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31913350 Free PMC article.
-
Role of GADD45A in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion through mediation of the JNK/p38 MAPK and STAT3/VEGF pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Dec;50(6):144. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5200. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36331027 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MAPK-ERK/JNK pathway: A potential intervention mechanism of myocardial fibrosis in heart failure.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Apr;173:116413. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116413. Epub 2024 Mar 9. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38461687 Review.
Cited by
-
Revealing the molecular links between coronary heart disease and cognitive impairment: the role of aging-related genes and therapeutic potential of stellate ganglion block.Biogerontology. 2024 Nov 28;26(1):16. doi: 10.1007/s10522-024-10159-x. Biogerontology. 2024. PMID: 39609308 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the SIRT3/SOD2 Signaling Pathway by a Compound Mixture from Polygonum orientale L. for Myocardial Damage.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;17(10):1288. doi: 10.3390/ph17101288. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong S.B., Hernández-Reséndiz S., Crespo-Avilan G.E., Mukhametshina R.T., Kwek X.Y., Cabrera-Fuentes H.A., Hausenloy D.J. Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction: Multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic opportunities. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018;186:73–87. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu Y., Yang M., Peng M., Xie L., Shen A., Lin S., Huang B., Chu J., Peng J. Kuanxiong aerosol inhibits apoptosis and attenuates isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury through the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021;269:113757. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113757. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

