Abscopal Effect, Extracellular Vesicles and Their Immunotherapeutic Potential in Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 37175226
- PMCID: PMC10180522
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093816
Abscopal Effect, Extracellular Vesicles and Their Immunotherapeutic Potential in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
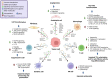
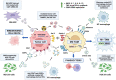
The communication between tumor cells and the microenvironment plays a fundamental role in the development, growth and further immune escape of the tumor. This communication is partially regulated by extracellular vesicles which can direct the behavior of surrounding cells. In recent years, it has been proposed that this feature could be applied as a potential treatment against cancer, since several studies have shown that tumors treated with radiotherapy can elicit a strong enough immune response to eliminate distant metastasis; this phenomenon is called the abscopal effect. The mechanism behind this effect may include the release of extracellular vesicles loaded with damage-associated molecular patterns and tumor-derived antigens which activates an antigen-specific immune response. This review will focus on the recent discoveries in cancer cell communications via extracellular vesicles and their implication in tumor development, as well as their potential use as an immunotherapeutic treatment against cancer.
Keywords: DAMPs; abscopal effect; cancer; extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Krieghoff-Henning E., Folkerts J., Penzkofer A., Weg-Remers S. Cancer—An overview. Med. Monatsschr. Pharm. 2017;40:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Sloan F.A., Gelband H., editors. Cancer Control Opportunities in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. The National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2007. The National Academies Collection: Reports Funded by National Institutes of Health. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

