Ultrasound-Microwave Combined Extraction of Novel Polysaccharide Fractions from Lycium barbarum Leaves and Their In Vitro Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities
- PMID: 37175290
- PMCID: PMC10180117
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093880
Ultrasound-Microwave Combined Extraction of Novel Polysaccharide Fractions from Lycium barbarum Leaves and Their In Vitro Hypoglycemic and Antioxidant Activities
Abstract
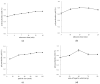
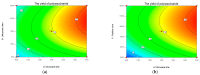
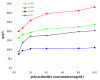
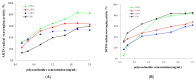
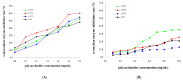
Ultrasound-microwave combined extraction (UMCE), gradient ethanol precipitation, chemical characterization, and antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of Lycium barbarum leaf polysaccharides (LLP) were systematically studied. The optimal conditions for UMCE of LLP achieved by response surface method (RSM) were as follows: microwave time of 16 min, ultrasonic time of 20 min, particle size of 100 mesh, and ratio of liquid to solid of 55:1. Three novel polysaccharide fractions (LLP30, LLP50, LLP70) with different molecular weights were obtained by gradient ethanol precipitation. Polysaccharide samples exhibited scavenging capacities against ABTS and DPPH radicals and inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase and α-amylase. Among the three fractions, LLP30 possessed relatively high antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities in vitro, which showed a potential for becoming a nutraceutical or a phytopharmaceutical for prevention and treatment of hyperglycemia or diabetes.
Keywords: Lycium barbarum leaves; antioxidant capacity; hypoglycemic activity; polysaccharides; ultrasound–microwave combined extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lee T.T.L., Hui J.M.H., Lee Y.H.A., Satti D.I., Shum Y.K.L., Kiu P.T.H., Wai A.K.C., Liu T., Wong W.T., Chan J.S.K., et al. Sulfonylurea is associated with higher risks of ventricular arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death compared with metformin: A population-based Cohort study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022;11:e026289. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang L., Hogan S., Li J.R., Sun S., Canning C., Zheng S.J., Zhou K.Q. Grape skin extract inhibits mammalian intestinal α-glucosidase activity and suppresses postprandial glycemic response in streptozonic-treated mice. Food Chem. 2011;126:466–471. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.11.016. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

