Preparation of Neohesperidin-Taro Starch Complex as a Novel Approach to Modulate the Physicochemical Properties, Structure and In Vitro Digestibility
- PMID: 37175311
- PMCID: PMC10179776
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28093901
Preparation of Neohesperidin-Taro Starch Complex as a Novel Approach to Modulate the Physicochemical Properties, Structure and In Vitro Digestibility
Abstract
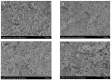
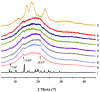
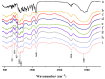
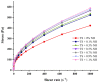
Neohesperidin (NH), a natural flavonoid, exerts multiple actions, such as antioxidant, antiviral, antiallergic, vasoprotective, anticarcinogenic and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as inhibition of tumor progression. In this study, the NH-taro starch complex is prepared, and the effects of NH complexation on the physicochemical properties, structure and in vitro digestibility of taro starch (TS) are investigated. Results showed that NH complexation significantly affected starch gelatinization temperatures and reduced its enthalpy value (ΔH). The addition of NH increased the viscosity and thickening of taro starch, facilitating shearing and thinning. NH binds to TS via hydrogen bonds and promotes the formation of certain crystalline regions in taro starch. SEM images revealed that the surface of NH-TS complexes became looser with the increasing addition of NH. The digestibility results demonstrated that the increase in NH (from 0.1% to 1.1%, weight based on starch) could raise RS (resistant starch) from 21.66% to 27.75% and reduce RDS (rapidly digestible starch) from 33.51% to 26.76% in taro starch. Our work provided a theoretical reference for the NH-taro starch complex's modification of physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility with potential in food and non-food applications.
Keywords: digestibility; neohesperidin; physicochemical; structure; taro starch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro starch digestibility, estimated glycemic index and antioxidant potential of taro (Colocasia esculenta L. Schott) corm.Food Chem. 2015 Feb 1;168:257-61. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.052. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25172708
-
Effect of high voltage dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) atmospheric cold plasma treatment on physicochemical and functional properties of taro (Colocasia esculenta) starch.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 2):126772. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126772. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37683744
-
Taro starch (Colocasia esculenta) and citric acid modified taro starch as tablet disintegrating agents.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Oct 15;118(Pt A):397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.086. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29935240
-
Taro starch: Isolation, morphology, modification and novel applications concern - A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 15;163:1283-1290. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.093. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32673724 Review.
-
Isolation, characterization, modification and uses of taro starch: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Dec 1;192:574-589. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.041. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34653440 Review.
References
-
- Iqbal S., Nadeem S., Bano R., Bahadur A., Ahmad Z., Javed M., AL-Anazy M.M., Qasier A.A., Laref A., Shoaib M., et al. Green synthesis of biodegradable terpolymer modified starch nanocomposite with carbon nanoparticles for food packaging application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021;138:50604. doi: 10.1002/app.50604. - DOI
-
- Iqbal S., Nadeem S., Bahadur A., Javed M., Ahmad Z., Ahmad M.N., Shoaib M., Liu G.C., Mohyuddin A., Raheel M. The Effect of Ni-Doped ZnO NPs on the Antibacterial Activity and Degradation Rate of Polyacrylic Acid-Modified Starch Nanocomposite. JOM. 2021;73:380–386. doi: 10.1007/s11837-020-04490-0. - DOI
-
- Zheng Y., Tian J., Kong X., Yang W., Yin X., Xu E., Chen S., Liu D., Ye X. Physicochemical and digestibility characterisation of maize starch–caffeic acid complexes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020;121:108857. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108857. - DOI
-
- Han X., Zhang M., Zhang R., Huang L., Jia X., Huang F., Liu L. Physicochemical interactions between rice starch and different polyphenols and structural characterization of their complexes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020;125:109227. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109227. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

