The Oligostilbene Gnetin H Is a Novel Glycolysis Inhibitor That Regulates Thioredoxin Interacting Protein Expression and Synergizes with OXPHOS Inhibitor in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 37175448
- PMCID: PMC10178141
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24097741
The Oligostilbene Gnetin H Is a Novel Glycolysis Inhibitor That Regulates Thioredoxin Interacting Protein Expression and Synergizes with OXPHOS Inhibitor in Cancer Cells
Abstract
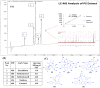
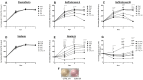
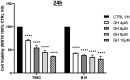
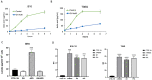
Since aerobic glycolysis was first observed in tumors almost a century ago by Otto Warburg, the field of cancer cell metabolism has sparked the interest of scientists around the world as it might offer new avenues of treatment for malignant cells. Our current study claims the discovery of gnetin H (GH) as a novel glycolysis inhibitor that can decrease metabolic activity and lactic acid synthesis and displays a strong cytostatic effect in melanoma and glioblastoma cells. Compared to most of the other glycolysis inhibitors used in combination with the complex-1 mitochondrial inhibitor phenformin (Phen), GH more potently inhibited cell growth. RNA-Seq with the T98G glioblastoma cell line treated with GH showed more than an 80-fold reduction in thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) expression, indicating that GH has a direct effect on regulating a key gene involved in the homeostasis of cellular glucose. GH in combination with phenformin also substantially enhances the levels of p-AMPK, a marker of metabolic catastrophe. These findings suggest that the concurrent use of the glycolytic inhibitor GH with a complex-1 mitochondrial inhibitor could be used as a powerful tool for inducing metabolic catastrophe in cancer cells and reducing their growth.
Keywords: Warburg effect; glycolysis; gnetin H; natural products; oligostilbene.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflict of interest and all the authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationship with organizations that could potentially be perceived as influencing the described research.
Figures
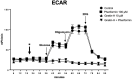


Similar articles
-
Genetic disruption of lactate/H+ symporters (MCTs) and their subunit CD147/BASIGIN sensitizes glycolytic tumor cells to phenformin.Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 1;75(1):171-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-2260. Epub 2014 Nov 17. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25403912
-
2-Deoxyglucose induces the expression of thioredoxin interacting protein (TXNIP) by increasing O-GlcNAcylation - Implications for targeting the Warburg effect in cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Oct 2;465(4):838-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.08.097. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26315267
-
TXNIP Links Anticipatory Unfolded Protein Response to Estrogen Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism in Breast Cancer Cells.Endocrinology. 2022 Jan 1;163(1):bqab212. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab212. Endocrinology. 2022. PMID: 34614512 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells: glycolysis, glutaminolysis, and Bcl-2 proteins as novel therapeutic targets for cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Jan 20;14(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0769-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26791262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxamate targeting aggressive cancers with special emphasis to brain tumors.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Mar;147:112686. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112686. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35124385 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress in antitumor mechanisms and applications of phenformin (Review).Oncol Rep. 2024 Nov;52(5):151. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8810. Epub 2024 Sep 20. Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39301645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Metabolism Therapy by Small Natural Compounds.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 7;24(18):13776. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813776. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762081 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction, purification, in vitro antioxidant and cytoprotective ability of oligostilbenes from paeonia seeds threshing residues.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 11;20(6):e0325485. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325485. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40498758 Free PMC article.
-
Cysteine protease inhibitor 1 promotes metastasis by mediating an oxidative phosphorylation/MEK/ERK axis in esophageal squamous carcinoma cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 29;14(1):4985. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55544-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38424293 Free PMC article.
-
The role of glycolysis in tumorigenesis: From biological aspects to therapeutic opportunities.Neoplasia. 2024 Dec;58:101076. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101076. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 39476482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

