Mesenchymal Stem Cell Behavior under Microgravity: From Stress Response to a Premature Senescence
- PMID: 37175460
- PMCID: PMC10178040
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24097753
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Behavior under Microgravity: From Stress Response to a Premature Senescence
Abstract
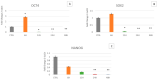
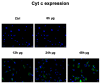
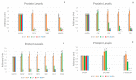
Mesenchymal stem cells are undifferentiated cells able to acquire different phenotypes under specific stimuli. Wharton's jelly is a tissue in the umbilical cord that contains mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) with a high plasticity and differentiation potential. Their regeneration capability is compromised by cell damage and aging. The main cause of cell damage is oxidative stress coming from an imbalance between oxidant and antioxidant species. Microgravity represents a stressing condition able to induce ROS production, ultimately leading to different subcellular compartment damages. Here, we analyzed molecular programs of stemness (Oct-4; SOX2; Nanog), cell senescence, p19, p21 (WAF1/CIP1), p53, and stress response in WJ-MSCs exposed to microgravity. From our results, we can infer that a simulated microgravity environment is able to influence WJ-MSC behavior by modulating the expression of stress and stemness-related genes, cell proliferation regulators, and both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic genes. Our results suggest a cellular adaptation addressed to survival occurring during the first hours of simulated microgravity, followed by a loss of stemness and proliferation capability, probably related to the appearance of a molecular program of senescence.
Keywords: cell senescence; cellular mechanisms; mesenchymal stem cells; microgravity; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Maioli M., Basoli V., Santaniello S., Cruciani S., Delitala A.P., Pinna R., Milia E., Grillari-Voglauer R., Fontani V., Rinaldi S., et al. Osteogenesis from Dental Pulp Derived Stem Cells: A Novel Conditioned Medium Including Melatonin within a Mixture of Hyaluronic, Butyric, and Retinoic Acids. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2056416. doi: 10.1155/2016/2056416. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim D.-W., Staples M., Shinozuka K., Pantcheva P., Kang S.-D., Borlongan C.V. Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Phenotypic Characterization and Optimizing Their Therapeutic Potential for Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013;14:11692. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611692. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rinaldi S., Maioli M., Santaniello S., Pigliaru G., Ventura C., Montela A., Sanna R., Bandiera P., Bagella L., Delitala A., et al. Amniotic fluid stem cells morph into a cardiovascular lineage: Analysis of a chemically induced cardiac and vascular commitment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013;7:1063–1073. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S44706. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

