The Epithelial Sodium Channel-An Underestimated Drug Target
- PMID: 37175488
- PMCID: PMC10178586
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24097775
The Epithelial Sodium Channel-An Underestimated Drug Target
Abstract
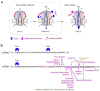
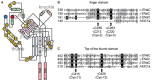
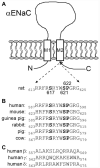
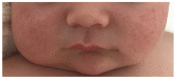
Epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) are part of a complex network of interacting biochemical pathways and as such are involved in several disease states. Dependent on site and type of mutation, gain- or loss-of-function generated symptoms occur which span from asymptomatic to life-threatening disorders such as Liddle syndrome, cystic fibrosis or generalized pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1. Variants of ENaC which are implicated in disease assist further understanding of their molecular mechanisms in order to create models for specific pharmacological targeting. Identification and characterization of ENaC modifiers not only furthers our basic understanding of how these regulatory processes interact, but also enables discovery of new therapeutic targets for the disease conditions caused by ENaC dysfunction. Numerous test compounds have revealed encouraging results in vitro and in animal models but less in clinical settings. The EMA- and FDA-designated orphan drug solnatide is currently being tested in phase 2 clinical trials in the setting of acute respiratory distress syndrome, and the NOX1/ NOX4 inhibitor setanaxib is undergoing clinical phase 2 and 3 trials for therapy of primary biliary cholangitis, liver stiffness, and carcinoma. The established ENaC blocker amiloride is mainly used as an add-on drug in the therapy of resistant hypertension and is being studied in ongoing clinical phase 3 and 4 trials for special applications. This review focuses on discussing some recent developments in the search for novel therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Liddle syndrome; TIP peptides; cystic fibrosis; epithelial sodium channel; gain- and loss-of-function mutations; pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1B; setanaxib; solnatide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In Liddle Syndrome, Epithelial Sodium Channel Is Hyperactive Mainly in the Early Part of the Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephron.Hypertension. 2016 Jun;67(6):1256-62. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.07061. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 27170740
-
[Regulation of kidney on potassium balance and its clinical significance].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2023 Apr 25;75(2):216-230. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37089096 Review. Chinese.
-
Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by membrane trafficking.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1802(12):1166-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.03.010. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20347969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aldosterone responsiveness of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in colon is increased in a mouse model for Liddle's syndrome.J Physiol. 2008 Jan 15;586(2):459-75. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.140459. Epub 2007 Nov 15. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18006588 Free PMC article.
-
Liddle syndrome due to a novel mutation in the γ subunit of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in family from Russia: a case report.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Oct 26;20(1):389. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1579-4. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31655555 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Dendritic cell epithelial sodium channel induced inflammation and salt-sensitive hypertension.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024 Mar 1;33(2):145-153. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000963. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38180118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lectin-like domain of TNF reduces pneumonia-induced injury in the perfused human lung.JCI Insight. 2025 Jun 9;10(11):e188325. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.188325. eCollection 2025 Jun 9. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40485585 Free PMC article.
-
The small molecule activator S3969 stimulates the epithelial sodium channel by interacting with a specific binding pocket in the channel's β-subunit.J Biol Chem. 2024 Apr;300(4):105785. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105785. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38401845 Free PMC article.
-
The Variety of Mechanosensitive Ion Channels in Retinal Neurons.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 30;25(9):4877. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094877. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38732096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of aldosterone to direct renin ratio, low renin and related Phenotypes in Afro-Colombian patients with apparent treatment resistant hypertension.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18091. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67261-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103362 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

