Alternative Splicing Changes Promoted by NOVA2 Upregulation in Endothelial Cells and Relevance for Gastric Cancer
- PMID: 37175811
- PMCID: PMC10178952
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24098102
Alternative Splicing Changes Promoted by NOVA2 Upregulation in Endothelial Cells and Relevance for Gastric Cancer
Abstract
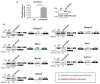
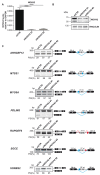
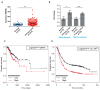
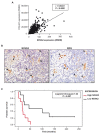
Angiogenesis is crucial for cancer progression. While several anti-angiogenic drugs are in use for cancer treatment, their clinical benefits are unsatisfactory. Thus, a deeper understanding of the mechanisms sustaining cancer vessel growth is fundamental to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Alternative splicing (AS) is an essential modifier of human proteome diversity. Nevertheless, AS contribution to tumor vasculature development is poorly known. The Neuro-Oncological Ventral Antigen 2 (NOVA2) is a critical AS regulator of angiogenesis and vascular development. NOVA2 is upregulated in tumor endothelial cells (ECs) of different cancers, thus representing a potential driver of tumor blood vessel aberrancies. Here, we identified novel AS transcripts generated upon NOVA2 upregulation in ECs, suggesting a pervasive role of NOVA2 in vascular biology. In addition, we report that NOVA2 is also upregulated in ECs of gastric cancer (GC), and its expression correlates with poor overall survival of GC patients. Finally, we found that the AS of the Rap Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor 6 (RapGEF6), a newly identified NOVA2 target, is altered in GC patients and associated with NOVA2 expression, tumor angiogenesis, and poor patient outcome. Our findings provide a better understanding of GC biology and suggest that AS might be exploited to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutics for anti-angiogenic GC treatments.
Keywords: RNA binding proteins; alternative splicing; angiogenesis; cancer biomarkers; gastric cancer; tumor vasculature.
Conflict of interest statement
Author C.G. has been involved as a consultant in Company Gene Tools, LLC. The funding sponsor had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis or interpretation of data and in the writing of the manuscript and the decision to publish it. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

