Coffee Staining and Simulated Brushing Induced Color Changes and Surface Roughness of 3D-Printed Orthodontic Retainer Material
- PMID: 37177310
- PMCID: PMC10180946
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15092164
Coffee Staining and Simulated Brushing Induced Color Changes and Surface Roughness of 3D-Printed Orthodontic Retainer Material
Abstract
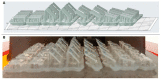
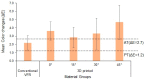
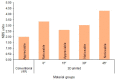
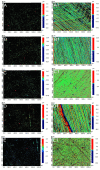
This in vitro study evaluated the influence of combined coffee staining and simulated brushing-induced color changes and surface roughness on 3D-printed orthodontic retainers. Specimens measuring 10 × 10 × 0.75 mm3 were obtained either by conventional vacuum forming or 3D printing at four print angulations (0°, 15°, 30°, and 45°) (n = 10). The prepared specimens were immersed in a coffee beverage and then mechanically brushed using a simulating device. The specimen's color difference (ΔE) and surface roughness (Ra) were quantified using a spectrophotometer and a non-contact profilometer, respectively. The highest and lowest mean ΔE values were recorded for the 3D-printed-45° (4.68 ± 2.07) and conventional (2.18 ± 0.87) groups, respectively. The overall mean comparison of ΔE between the conventional and 3D-printed groups was statistically significant (p < 0.01). After simulated brushing, all groups showed a statistically significant increase in the Ra values (p < 0.01). The highest Ra was in the 3D-printed-45° (1.009 ± 0.13 µm) and conventional (0.743 ± 0.12 µm) groups, respectively. The overall ΔE of 3D-printed orthodontic retainers was not comparable to conventional VFRs. Among the different angulations used to print the retainers, 15° angulations were the most efficient in terms of color changes and surface roughness and were comparable to conventional VFRs.
Keywords: 3D printing; color; orthodontic retainer; stereolithography; surface roughness; tooth brushing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Anil P. Fixed Retention in Orthodontics. Decis. Dent. 2019;5:21–22.
-
- Shopova D., Yordanova M., Yordanova S. Capabilities of Digital Software for Creating a 3D Printed Retainer. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2022;10:6–10. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2022.7874. - DOI
-
- Alshahrani I., Asiry M.A., Altwijry M.K., Premanath S.N., Ramakrishnaiah R., Durgesh B.H. Nanomechanical properties, surface topography, and color stability of fiber-reinforced composite orthodontic retainers. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2019;27:92–100. doi: 10.1177/0967391118819703. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

