Flamingo-Optimization-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network for IoT-Based Arrhythmia Classification
- PMID: 37177564
- PMCID: PMC10181507
- DOI: 10.3390/s23094353
Flamingo-Optimization-Based Deep Convolutional Neural Network for IoT-Based Arrhythmia Classification
Abstract
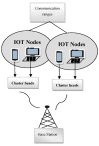
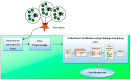
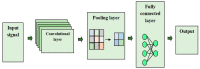
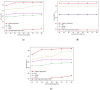
Cardiac arrhythmia is a deadly disease that threatens the lives of millions of people, which shows the need for earlier detection and classification. An abnormal signal in the heart causing arrhythmia can be detected at an earlier stage when the health data from the patient are monitored using IoT technology. Arrhythmias may suddenly lead to death and the classification of arrhythmias is considered a complicated process. In this research, an effective classification model for the classification of heart disease is developed using flamingo optimization. Initially, the ECG signal from the heart is collected and then it is subjected to the preprocessing stage; to detect and control the electrical activity of the heart, the electrocardiogram (ECG) is used. The input signals collected using IoT nodes are collectively presented in the base station for the classification using flamingo-optimization-based deep convolutional networks, which effectively predict the disease. With the aid of communication technologies and the contribution of IoT, medical professionals can easily monitor the health condition of patients. The performance is analyzed in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity.
Keywords: DCNN; ECG signal; IoT nodes; arrhythmia classification; flamingo optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
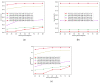
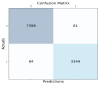
Similar articles
-
Arrhythmia Classification with ECG signals based on the Optimization-Enabled Deep Convolutional Neural Network.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Nov;196:105607. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105607. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32593973
-
[Deep residual convolutional neural network for recognition of electrocardiogram signal arrhythmias].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 25;36(2):189-198. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.201712031. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31016934 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Arrhythmia detection using deep convolutional neural network with long duration ECG signals.Comput Biol Med. 2018 Nov 1;102:411-420. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Comput Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30245122
-
An Improved Convolutional Neural Network Based Approach for Automated Heartbeat Classification.J Med Syst. 2019 Dec 18;44(2):35. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1511-2. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 31853698
-
Deep learning for ECG Arrhythmia detection and classification: an overview of progress for period 2017-2023.Front Physiol. 2023 Sep 15;14:1246746. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1246746. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37791347 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Automated Arrhythmia Classification Using Farmland Fertility Algorithm with Hybrid Deep Learning Model on Internet of Things Environment.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 6;23(19):8265. doi: 10.3390/s23198265. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37837102 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and Limitation Analysis of an IoT-Dependent System for Deployment in Smart Healthcare Using Communication Standards Features.Sensors (Basel). 2023 May 28;23(11):5155. doi: 10.3390/s23115155. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J., Rong J., Sun L., Wang H., Zhang Y., Ma J. A framework for cardiac arrhythmia detection from IoT-based ECGs. World Wide Web. 2020;23:2835–2850. doi: 10.1007/s11280-019-00776-9. - DOI
-
- Devi R.L., Kalaivani V. Machine learning and IoT-based cardiac arrhythmia diagnosis using statistical and dynamic features of ECG. J. Supercomput. 2020;76:6533–6544. doi: 10.1007/s11227-019-02873-y. - DOI
-
- Hammad M., Iliyasu A.M., Subasi A., Ho E.S., Abd El-Latif A.A. A multitier deep learning model for arrhythmia detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020;70:1–9. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3033072. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

