Multi-Transduction-Mechanism Technology, an Emerging Approach to Enhance Sensor Performance
- PMID: 37177661
- PMCID: PMC10181588
- DOI: 10.3390/s23094457
Multi-Transduction-Mechanism Technology, an Emerging Approach to Enhance Sensor Performance
Abstract
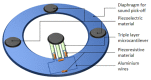
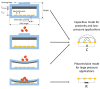
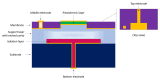
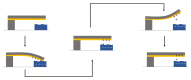
Conventional sensor systems employ single-transduction technology where they respond to an input stimulus and transduce the measured parameter into a readable output signal. As such, the technology can only provide limited corresponding data of the detected parameters due to relying on a single transformed output signal for information acquisition. This limitation commonly results in the need for utilizing sensor array technology to detect targeted parameters in complex environments. Multi-transduction-mechanism technology, on the other hand, may combine more than one transduction mechanism into a single structure. By employing this technology, sensors can be designed to simultaneously distinguish between different input signals from complex environments for greater degrees of freedom. This allows a multi-parameter response, which results in an increased range of detection and improved signal-to-noise ratio. In addition, utilizing a multi-transduction-mechanism approach can achieve miniaturization by reducing the number of required sensors in an array, providing further miniaturization and enhanced performance. This paper introduces the concept of multi-transduction-mechanism technology by exploring different candidate combinations of fundamental transduction mechanisms such as piezoresistive, piezoelectric, triboelectric, capacitive, and inductive mechanisms.
Keywords: capacitive; electronic nose; energy harvesting; hybrid nanogenerators; microelectromechanical systems; multi-transduction; piezoelectric; sensor; transduction mechanisms; triboelectric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Sinclair I.R. Sensors and Transducers. 3rd ed. Newnes; London, UK: 2001.
-
- Gong S., Zhang B., Zhang J., Lin Wang Z., Ren K., Gong S., Zhang B., Zhang J., Wang Z.L., Ren K. Biocompatible Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Hybrid Piezoelectric and Electret Nanogenerator for Electronic Skin Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:1908724. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201908724. - DOI
-
- Kumaresan Y., Ozioko O., Dahiya R. Effect of Dielectric and Stiffness of Soft Material between the Electrodes of a Capacitive Pressure Sensor on Its Performance; Proceedings of the FLEPS 2020—IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems; Manchester, UK. 16–19 August 2020; - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

