GluD receptors are functional ion channels
- PMID: 37177782
- PMCID: PMC10323023
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.05.012
GluD receptors are functional ion channels
Abstract
In this article, we review contemporary evidence that GluD receptors are functional ion channels whose depolarizing currents contribute to their biological functions, akin to all other members of the ionotropic glutamate receptor (iGluR) family.
Copyright © 2023 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
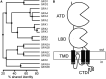
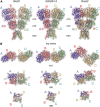
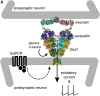
References
-
- Watkins J.C., Evans R.H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. 1981;21:165–204. - PubMed
-
- Hollmann M., Heinemann S. Cloned glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1994;17:31–108. - PubMed
-
- Stroebel D., Mony L., Paoletti P. Glycine agonism in ionotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2021;193 - PubMed
-
- Araki K., Meguro H., et al. Mishina M. Selective expression of the glutamate receptor channel delta 2 subunit in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993;197:1267–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

