PTB-XL+, a comprehensive electrocardiographic feature dataset
- PMID: 37179420
- PMCID: PMC10183020
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02153-8
PTB-XL+, a comprehensive electrocardiographic feature dataset
Abstract
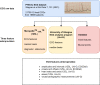
Machine learning (ML) methods for the analysis of electrocardiography (ECG) data are gaining importance, substantially supported by the release of large public datasets. However, these current datasets miss important derived descriptors such as ECG features that have been devised in the past hundred years and still form the basis of most automatic ECG analysis algorithms and are critical for cardiologists' decision processes. ECG features are available from sophisticated commercial software but are not accessible to the general public. To alleviate this issue, we add ECG features from two leading commercial algorithms and an open-source implementation supplemented by a set of automatic diagnostic statements from a commercial ECG analysis software in preprocessed format. This allows the comparison of ML models trained on clinically versus automatically generated label sets. We provide an extensive technical validation of features and diagnostic statements for ML applications. We believe this release crucially enhances the usability of the PTB-XL dataset as a reference dataset for ML methods in the context of ECG data.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Dagenais, G. R. et al. Variations in common diseases, hospital admissions, and deaths in middle-aged adults in 21 countries from five continents (PURE): a prospective cohort study. The Lancet (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

