Adsorption and Dissociation of R-Methyl p-Tolyl Sulfoxide on Au(111)
- PMID: 37179596
- PMCID: PMC10173319
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01647
Adsorption and Dissociation of R-Methyl p-Tolyl Sulfoxide on Au(111)
Abstract
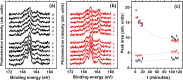
Sulfur-based molecules producing self-assembled monolayers on gold surfaces have long since become relevant functional molecular materials with many applications in biosensing, electronics, and nanotechnology. Among the various sulfur-containing molecules, the possibility to anchor a chiral sulfoxide to a metal surface has been scarcely investigated, despite this class of molecules being of great importance as ligands and catalysts. In this work, (R)-(+)-methyl p-tolyl sulfoxide was deposited on Au(111) and investigated by means of photoelectron spectroscopy and density functional theory calculations. The interaction with Au(111) leads to a partial dissociation of the adsorbate due to S-CH3 bond cleavage. The observed kinetics support the hypotheses that (R)-(+)-methyl p-tolyl sulfoxide adsorbs on Au(111) in two different adsorption arrangements endowed with different adsorption and reaction activation energies. The kinetic parameters related to the adsorption/desorption and reaction of the molecule on the Au(111) surface have been estimated.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Singh M.; Kaur N.; Comini E. Role of Self-Assembled Monolayers in Electronic Devices. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3938–3955. 10.1039/D0TC00388C. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

