Optical Immunosensor for the Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Food Matrixes
- PMID: 37179640
- PMCID: PMC10173425
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c07848
Optical Immunosensor for the Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in Food Matrixes
Abstract
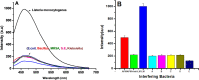
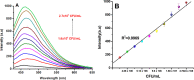
In this paper, simple imine-based organic fluorophore 4-amino-3-(anthracene-9 yl methyleneamino) phenyl (phenyl) methanone (APM) has been synthesized via a greener approach and the same was used to construct a fluorescent immunoassay for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes (LM). A monoclonal antibody of LM was tagged with APM via the conjugation of the amine group in APM and the acid group of anti-LM through EDC/NHS coupling. The designed immunoassay was optimized for the specific detection of LM in the presence of other interfering pathogens based on the aggregation-induced emission mechanism and the formation of aggregates and their morphology was confirmed with the help of scanning electron microscopy. Density functional theory studies were done to further support the sensing mechanism-based changes in the energy level distribution. All photophysical parameters were measured by using fluorescence spectroscopy techniques. Specific and competitive recognition of LM was done in the presence of other relevant pathogens. The immunoassay shows a linear appreciable range from 1.6 × 106-2.7024 × 108 cfu/mL using the standard plate count method. The LOD has been calculated from the linear equation and the value is found as 3.2 cfu/mL, and this is the lowest LOD value reported for the detection of LM so far. The practical applications of the immunoassay were demonstrated in various food samples, and their accuracy obtained was highly comparable with the standard existing ELISA method.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
First organic fluorescence immunoassay for the detection of Enterobacter cloacae in food matrixes.Anal Methods. 2024 Jun 20;16(24):3927-3937. doi: 10.1039/d4ay00289j. Anal Methods. 2024. PMID: 38832637
-
Fluorescence immunoassay for the targeted determination of trace Listeria monocytogenes based on immunomagnetic separation and CdZnTe quantum dot indication.Anal Methods. 2022 Mar 17;14(11):1124-1133. doi: 10.1039/d1ay02106k. Anal Methods. 2022. PMID: 35212322
-
Layer-by-layer assembly of polyoxometalate-pyrene-decorated fluorescent microspheres for the suspension immunoassay of Listeria monocytogenes.J Mater Chem B. 2016 Jun 28;4(24):4287-4294. doi: 10.1039/c6tb00986g. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Mater Chem B. 2016. PMID: 32263410
-
[Comparison of direct colony count methods and the MPN-method for quantitative detection of Listeria in model and field conditions].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2001 Nov-Dec;114(11-12):453-64. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2001. PMID: 11766274 Review. German.
-
Detection and Potential Virulence of Viable but Non-Culturable (VBNC) Listeria monocytogenes: A Review.Microorganisms. 2021 Jan 19;9(1):194. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010194. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33477778 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chiriacò M.; Parlangeli I.; Sirsi F.; Poltronieri P.; Primiceri E. Impedance Sensing Platform for Detection of the Food Pathogen Listeria Monocytogenes. Electron 2018, 7, 347.10.3390/electronics7120347. - DOI
-
- Wang W.; Liu L.; Song S.; Xu L.; Zhu J.; Kuang H. Gold nanoparticle-based paper sensor for multiple detection of 12 Listeria spp. by P60-mediated monoclonal antibody. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 274–287. 10.1080/09540105.2016.1263986. - DOI
-
- Kayode A. J.; Igbinosa E. O.; Okoh A. I. Overview of listeriosis in the Southern African Hemisphere-Review. J. Food Saf. 2020, 40, e1273210.1111/jfs.12732. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

