Electroactive nanofibrous membrane with temperature monitoring for wound healing
- PMID: 37179989
- PMCID: PMC10170354
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra01665j
Electroactive nanofibrous membrane with temperature monitoring for wound healing
Abstract
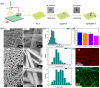
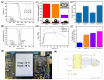
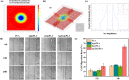
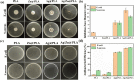
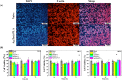
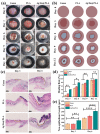
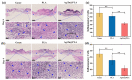
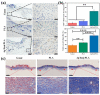
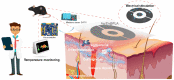
Developing functional dressings for promoting cellular activities and monitoring the healing progress is receiving increasingly widespread attention. In this study, Ag/Zn electrodes were deposited on the surface of a polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibrous membrane which can mimic the extracellular matrix. When wetted by wound exudate, the Ag/Zn electrodes could generate an electric stimulation (ES), promoting the migration of fibroblasts that heal wounds. Moreover, the Ag/Zn@PLA dressing showed excellent antibacterial activity against E. coli (95%) and S. aureus (97%). The study found that the electrostatic (ES) effect and the release of metal ions mainly contribute to the wound healing properties of Ag/Zn@PLA. In vivo mouse models demonstrated that Ag/Zn@PLA could promote wound healing by improving re-epithelialization, collagen deposition, and neovascularization. Additionally, the integrated sensor within the Ag/Zn@PLA dressing can monitor the wound site's temperature in real-time, providing timely information on wound inflammatory reactions. Overall, this work suggests that combining electroactive therapy and wound temperature monitoring may provide a new strategy for designing functional wound dressings.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Yang Y. Du Y. Zhang J. Zhang H. Guo B. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022;4:1027–1057.
-
- Wang C. Liang Y. Huang Y. Li M. Guo B. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022;121:207–219.
-
- Wu K. Yang Q. Zhang L. Xu P. Wu X. Yang H. Zhou H. Lin X. Yang L. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023;133:123–134.
-
- Yu L. Zhang H. Xiao L. Fan J. Li T. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022;14:21814–21821. - PubMed
-
- Liang J. Zeng H. Qiao L. Jiang H. Ye Q. Wang Z. Liu B. Fan Z. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022;14:30507–30522. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

