Combining immunotherapy and radiotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: the importance of irradiated tumor burden and the possible role of a low dose radiotherapy induction strategy
- PMID: 37180671
- PMCID: PMC10174792
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-23-192
Combining immunotherapy and radiotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: the importance of irradiated tumor burden and the possible role of a low dose radiotherapy induction strategy
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); checkpoint inhibition; combination therapy; radiotherapy (RT); tumor burden.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tcr-23-192/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
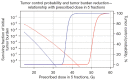
Comment on
-
Phase 1 Randomized Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Followed by Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Advanced/Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Jan 1;115(1):202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.09.052. Epub 2022 Sep 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 36108891 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Juloori A, Katipally RR, Lemons JM, et al. Phase 1 Randomized Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Followed by Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Advanced/Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2023;115:202-13. 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.09.052 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
